Interleukin-37 promotes colitis-associated carcinogenesis via SIGIRR-mediated cytotoxic T cells dysfunction
- PMID: 35046386
- PMCID: PMC8770466
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-021-00820-z
Interleukin-37 promotes colitis-associated carcinogenesis via SIGIRR-mediated cytotoxic T cells dysfunction
Abstract
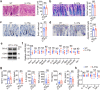
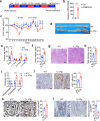
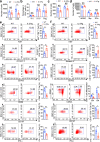
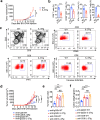
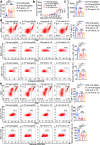
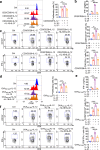
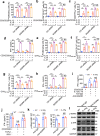
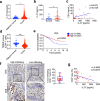
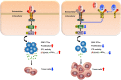
Interleukin-37b (hereafter called IL-37) was identified as fundamental inhibitor of natural and acquired immunity. The molecular mechanism and function of IL-37 in colorectal cancer (CRC) has been elusive. Here, we found that IL-37 transgenic (IL-37tg) mice were highly susceptible to colitis-associated colorectal cancer (CAC) and suffered from dramatically increased tumor burdens in colon. Nevertheless, IL-37 is dispensable for intestinal mutagenesis, and CRC cell proliferation, apoptosis, and migration. Notably, IL-37 dampened protective cytotoxic T cell-mediated immunity in CAC and B16-OVA models. CD8+ T cell dysfunction is defined by reduced retention and activation as well as failure to proliferate and produce cytotoxic cytokines in IL-37tg mice, enabling tumor evasion of immune surveillance. The dysfunction led by IL-37 antagonizes IL-18-induced proliferation and effector function of CD8+ T cells, which was dependent on SIGIRR (single immunoglobulin interleukin-1 receptor-related protein). Finally, we observed that IL-37 levels were significantly increased in CRC patients, and positively correlated with serum CRC biomarker CEA levels, but negatively correlated with the CD8+ T cell infiltration in CRC patients. Our findings highlight the role of IL-37 in harnessing antitumor immunity by inactivation of cytotoxic T cells and establish a new defined inhibitory factor IL-37/SIGIRR in cancer-immunity cycle as therapeutic targets in CRC.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Arnold M, et al. Global patterns and trends in colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut. 2017;66:683–691. - PubMed
-
- Pages F, et al. International validation of the consensus Immunoscore for the classification of colon cancer: a prognostic and accuracy study. Lancet. 2018;391:2128–2139. - PubMed
-
- Pages F, et al. In situ cytotoxic and memory T cells predict outcome in patients with early-stage colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009;27:5944–5951. - PubMed
-
- Xue J, et al. Intrinsic beta-catenin signaling suppresses CD8(+) T-cell infiltration in colorectal cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019;115:108921. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

