Androgens increase excitatory neurogenic potential in human brain organoids
- PMID: 35046577
- PMCID: PMC7612328
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-04330-4
Androgens increase excitatory neurogenic potential in human brain organoids
Abstract
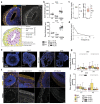
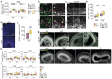
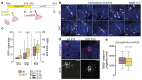
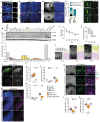
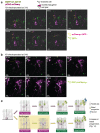
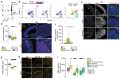
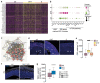
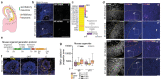
The biological basis of male-female brain differences has been difficult to elucidate in humans. The most notable morphological difference is size, with male individuals having on average a larger brain than female individuals1,2, but a mechanistic understanding of how this difference arises remains unknown. Here we use brain organoids3 to show that although sex chromosomal complement has no observable effect on neurogenesis, sex steroids-namely androgens-lead to increased proliferation of cortical progenitors and an increased neurogenic pool. Transcriptomic analysis and functional studies demonstrate downstream effects on histone deacetylase activity and the mTOR pathway. Finally, we show that androgens specifically increase the neurogenic output of excitatory neuronal progenitors, whereas inhibitory neuronal progenitors are not increased. These findings reveal a role for androgens in regulating the number of excitatory neurons and represent a step towards understanding the origin of sex-related brain differences in humans.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
M.A.L. is an inventor on several patents related to cerebral organoids, is co-founder and scientific advisory board member of a:head bio, and scientific advisory board member of the Roche Institute for Translational Bioengineering.
Figures




Comment in
-
Androgen signal for brain size.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2022 Apr;23(4):188-189. doi: 10.1038/s41583-022-00571-y. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35190708 No abstract available.
-
Androgens increase excitement in brain organoid research.Cell Stem Cell. 2022 Apr 7;29(4):495-497. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2022.02.012. Cell Stem Cell. 2022. PMID: 35395183
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

