Cigarette Smoke Particle-Induced Lung Injury and Iron Homeostasis
- PMID: 35046648
- PMCID: PMC8763205
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S337354
Cigarette Smoke Particle-Induced Lung Injury and Iron Homeostasis
Abstract
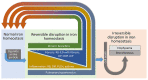
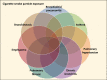
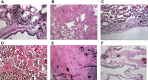
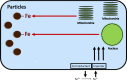
It is proposed that the mechanistic basis for non-neoplastic lung injury with cigarette smoking is a disruption of iron homeostasis in cells after exposure to cigarette smoke particle (CSP). Following the complexation and sequestration of intracellular iron by CSP, the host response (eg, inflammation, mucus production, and fibrosis) attempts to reverse a functional metal deficiency. Clinical manifestations of this response can present as respiratory bronchiolitis, desquamative interstitial pneumonitis, pulmonary Langerhans' cell histiocytosis, asthma, pulmonary hypertension, chronic bronchitis, and pulmonary fibrosis. If the response is unsuccessful, the functional deficiency of iron progresses to irreversible cell death evident in emphysema and bronchiectasis. The subsequent clinical and pathological presentation is a continuum of lung injuries, which overlap and coexist with one another. Designating these non-neoplastic lung injuries after smoking as distinct disease processes fails to recognize shared relationships to each other and ultimately to CSP, as well as the common mechanistic pathway (ie, disruption of iron homeostasis).
Keywords: chronic bronchitis; ferritins; hypertension, pulmonary; iron; pulmonary disease, chronic obstructive; pulmonary emphysema; pulmonary fibrosis.
© 2022 Ghio et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
-
- National Research Council. Environmental Tobacco Smoke: Measuring Exposures and Assessing Health Effects. Washington DC: National Academy Press; 1986. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

