AKAP9 Upregulation Predicts Unfavorable Prognosis in Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Promotes Stemness Properties via the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway
- PMID: 35046723
- PMCID: PMC8760470
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S343033
AKAP9 Upregulation Predicts Unfavorable Prognosis in Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Promotes Stemness Properties via the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway
Abstract
Background: PRKA kinase anchor protein 9 (AKAP9) is a scaffold protein involved in various cellular processes, including cell adhesion, proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Although the oncogenic role of AKAP9 in solid tumors is well elucidated, the functions and mechanisms of AKAP9 in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) are still not understood.
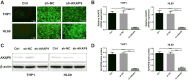
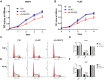
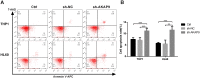
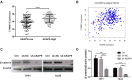
Methods: We used the gene expression omnibus (GEO) database (GSE2191) to determine the mRNA expression of AKAP9 in the bone marrow of pediatric AML and healthy patients. We further used the therapeutically available research to generate effective treatments (TARGET) database to elucidate the relationship between AKAP9 expression and clinical outcomes in pediatric patients with AML. In addition, cell proliferation, cell cycle, apoptosis, RT-PCR, and Western blotting assays were applied to reveal the functions of AKAP9 and the underlying mechanisms of AKAP9 silencing in THP1 and HL60 cell lines.
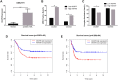
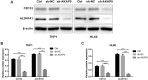
Results: AKAP9 is overexpressed in the bone marrow of pediatric AML patients as compared with that of healthy patients. High expression of AKAP9 was found to be a predictor of poor overall survival (OS) and event-free survival (EFS). Using univariate and multivariate survival analyses, we found that high AKAP9 expression is an independent predictor of a worse OS and EFS. Functionally, AKAP9 silencing significantly inhibited AML cell proliferation, and cell cycle progression and promoted apoptosis. Moreover, AKAP9 silencing significantly downregulated the expression of stemness markers and β-catenin.
Conclusion: AKAP9 upregulation is a predictor of unfavorable prognosis, promotes stemness, and activates the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in AML patients. AKAP9 may act as a prognostic biomarker of AML in pediatric patients and a future therapeutic target.
Keywords: PRKA kinase anchor protein 9; acute myeloid leukemia; leukemic stem cells; pediatric; prognosis.
© 2022 Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
High expression of malic enzyme 1 predicts adverse prognosis in patients with cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukaemia and promotes leukaemogenesis through the IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 pathways.Ther Adv Hematol. 2024 Nov 27;15:20406207241301948. doi: 10.1177/20406207241301948. eCollection 2024. Ther Adv Hematol. 2024. PMID: 39610460 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of Wnt/β-Catenin Exerts Antileukemia Activity and Synergizes with FLT3 Inhibition in FLT3-Mutant Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Clin Cancer Res. 2018 May 15;24(10):2417-2429. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-1556. Epub 2018 Feb 20. Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29463558 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA-DUXAP8 Regulation of the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway to Inhibit Glycolysis and Induced Apoptosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Turk J Haematol. 2021 Dec 7;38(4):264-272. doi: 10.4274/tjh.galenos.2021.2020.0769. Epub 2021 Aug 25. Turk J Haematol. 2021. PMID: 34431643 Free PMC article.
-
High NCALD expression predicts poor prognosis of cytogenetic normal acute myeloid leukemia.J Transl Med. 2019 May 20;17(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-1904-5. J Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31109331 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of SPINK2 in acute myeloid leukemia.Adv Lab Med. 2023 Feb 20;4(1):92-104. doi: 10.1515/almed-2022-0047. eCollection 2023 Apr. Adv Lab Med. 2023. PMID: 37359898 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Acute myeloid leukemia with a novel AKAP9::PDGFRA fusion transformed from essential thrombocythemia: A case report and mini review.Leuk Res Rep. 2024 May 31;21:100465. doi: 10.1016/j.lrr.2024.100465. eCollection 2024. Leuk Res Rep. 2024. PMID: 38952949 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of RASSF1A, DIRAS3, and AKAP9 Genes in Thyroid Lesions: Implications for Differential Diagnosis and Prognosis of Thyroid Carcinomas.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 1;25(1):562. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010562. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38203733 Free PMC article.
-
Fucoxanthin inhibits the proliferation of MOLM13 cells by targeting AKT to disrupt glucose metabolism.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 15;16:1601281. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1601281. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40735485 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

