Spatial Distribution and Predictive Significance of Dendritic Cells and Macrophages in Esophageal Cancer Treated With Combined Chemoradiotherapy and PD-1 Blockade
- PMID: 35046943
- PMCID: PMC8761740
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.786429
Spatial Distribution and Predictive Significance of Dendritic Cells and Macrophages in Esophageal Cancer Treated With Combined Chemoradiotherapy and PD-1 Blockade
Abstract
Background: The first clinical study (NCT03671265) of first-line chemoradiotherapy combined with PD-1 blockade showed promising treatment outcomes in locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). However, partial patients did not respond to the combination treatment. The roles of dendritic cells (DCs) and macrophages in this combination treatment remain poorly understood.
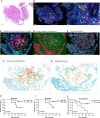
Methods: We performed multiplexed immunofluorescence method to identify CD11c+ DCs, CD68+ macrophages, and their PD-L1- or PD-L1+ subpopulations in paired tumor biopsies (n = 36) collected at baseline and during the combination treatment (after radiation, 40 Gy) from the phase Ib trial (NCT03671265). We applied whole exome sequencing in the baseline tumor biopsies (n = 14) to estimate tumor mutation burden (TMB). We dynamically investigated the spatial distribution of DCs and macrophages under chemoradiotherapy combined with PD-1 blockade, and evaluated the association between their spatial distribution and combination outcome, and TMB.
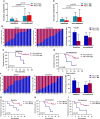
Results: The results showed that high percentages of PD-L1- DCs and macrophages in the baseline tumor compartment, but not in the stromal compartment, predicted improved OS and PFS. Chemoradiotherapy combined with PD-1 blockade promoted DCs and macrophages to migrate closer to tumor cells. During combination treatment, PD-L1- tumor cells were nearest to PD-L1- DCs and macrophages, while PD-L1+ tumor cells were next to PD-L1+ DCs and macrophages. High TMB was closely associated with a shorter distance from tumor cells to DCs and macrophages. Shorter distance between PD-L1+ tumor cells and PD-L1+ DCs or PD-L1- macrophages during the combination was correlated with better OS. Shorter distance between PD-L1- tumor cells and PD-L1- macrophages during combination was associated with both longer OS and PFS.
Conclusions: PD-L1- or PD-L1+ DCs and macrophages exhibit distinct spatial distribution in ESCC. The close distance between tumor cells and these antigen-presenting cells (APCs) is critical to the clinical outcome in chemoradiotherapy combined with PD-1 blockade in ESCC patients. Our results highlight the predictive potential of spatial patterns of APCs in chemoradiotherapy combined with immunotherapy and reveal the underlying mechanism of APCs participating in chemoradiotherapy-induced antitumor immune response in ESCC.
Keywords: PD-1; chemoradiotherapy; dendritic cell; esophageal cancer; immunofluorescence; macrophage; spatial; tumor mutation burden.
Copyright © 2022 Ma, Guo, Wei, Zhao, Han, Zhang, Chen, Cao, Dong, Zhao, Yuan, Wang, Pang, Yan and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Fukushima H, Yoshida S, Kijima T, Nakamura Y, Fukuda S, Uehara S, et al. . Combination of Cisplatin and Irradiation Induces Immunogenic Cell Death and Potentiates Postirradiation Anti-PD-1 Treatment Efficacy in Urothelial Carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci (2021) 22(2):535. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020535 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jabbour SK, Berman AT, Decker RH, Lin Y, Feigenberg SJ, Gettinger SN, et al. . Phase 1 Trial of Pembrolizumab Administered Concurrently With Chemoradiotherapy for Locally Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Nonrandomized Controlled Trial. JAMA Oncol (2020) 6(6):848–55. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.6731 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang W, Yan C, Zhang T, Chen X, Dong J, Zhao J, et al. . Addition of Camrelizumab to Docetaxel, Cisplatin, and Radiation Therapy in Patients With Locally Advanced Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Phase 1b Study. OncoImmunology (2021) 10(1):1971418. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2021.1971418 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Qian D, Wang Y, Zhao G, Cao F, Er P, Chen X, et al. . Tumor Remission and Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes During Chemoradiation Therapy: Predictive and Prognostic Markers in Locally Advanced Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys (2019) 105(2):319–28. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.06.079 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

