STAT6/VDR Axis Mitigates Lung Inflammatory Injury by Promoting Nrf2 Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 35047105
- PMCID: PMC8763503
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2485250
STAT6/VDR Axis Mitigates Lung Inflammatory Injury by Promoting Nrf2 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
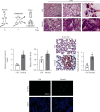
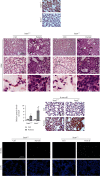
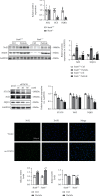
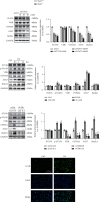
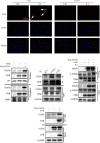
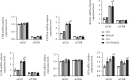
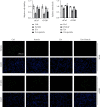
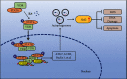
Lung inflammatory injury is a global public health concern. It is characterized by infiltration of diverse inflammatory cells and thickening of pulmonary septum along with oxidative stress to airway epithelial cells. STAT6 is a nuclear transcription factor that plays a crucial role in orchestrating the immune response, but its function in tissue inflammatory injury has not been comprehensively studied. Here, we demonstrated that STAT6 activation can protect against particle-induced lung inflammatory injury by resisting oxidative stress. Specifically, genetic ablation of STAT6 was observed to worsen particle-induced lung injury mainly by disrupting the lungs' antioxidant capacity, as reflected by the downregulation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway, an increase in malondialdehyde levels, and a decrease in glutathione levels. Vitamin D receptor (VDR) has been previously proved to positively regulate Nrf2 signals. In this study, silencing VDR expression in human bronchial epithelial BEAS-2B cells consistently suppressed autophagy-mediated activation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway, thereby aggravating particle-induced cell damage. Mechanically, STAT6 activation promoted the nuclear translocation of VDR, which increased the transcription of autophagy-related genes and induced Nrf2 signals, and silencing VDR abolished these effects. Our research provides important insights into the role of STAT6 in oxidative damage and reveals its potential underlying mechanism. This information not only deepens the appreciation of STAT6 but also opens new avenues for the discovery of therapies for inflammatory respiratory system disorders.
Copyright © 2022 Youjing Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Irisin drives macrophage anti-inflammatory differentiation via JAK2-STAT6-dependent activation of PPARγ and Nrf2 signaling.Free Radic Biol Med. 2023 May 20;201:98-110. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.03.014. Epub 2023 Mar 20. Free Radic Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 36940733
-
Vitamin D protects silica particles induced lung injury by promoting macrophage polarization in a KLF4-STAT6 manner.J Nutr Biochem. 2022 Dec;110:109148. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2022.109148. Epub 2022 Aug 29. J Nutr Biochem. 2022. PMID: 36049670
-
14,15-Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid suppresses cigarette smoke condensate-induced inflammation in lung epithelial cells by inhibiting autophagy.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016 Nov 1;311(5):L970-L980. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00161.2016. Epub 2016 Sep 2. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27591243
-
The role of nuclear factor-erythroid 2 related factor 2 (Nrf-2) in the protection against lung injury.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017 Feb 1;312(2):L155-L162. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00449.2016. Epub 2016 Nov 18. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27864288 Review.
-
[Recent advances in the study of Nrf2 and inflammatory respiratory diseases].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2015 Sep;50(9):1080-7. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2015. PMID: 26757542 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Vitamin D Improves Cognitive Impairment and Alleviates Ferroptosis via the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Aging Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 18;24(20):15315. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015315. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894993 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Quezada-Maldonado E. M., Sánchez-Pérez Y., Chirino Y. I., García-Cuellar C. M. Airborne particulate matter induces oxidative damage, DNA adduct formation and alterations in DNA repair pathways. Environmental Pollution . 2021;2021(287, article 117313) - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

