Altered BMP2/4 Signaling in Stem Cells and Their Niche: Different Cancers but Similar Mechanisms, the Example of Myeloid Leukemia and Breast Cancer
- PMID: 35047500
- PMCID: PMC8762220
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.787989
Altered BMP2/4 Signaling in Stem Cells and Their Niche: Different Cancers but Similar Mechanisms, the Example of Myeloid Leukemia and Breast Cancer
Abstract
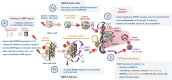
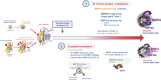
Understanding mechanisms of cancer development is mandatory for disease prevention and management. In healthy tissue, the microenvironment or niche governs stem cell fate by regulating the availability of soluble molecules, cell-cell contacts, cell-matrix interactions, and physical constraints. Gaining insight into the biology of the stem cell microenvironment is of utmost importance, since it plays a role at all stages of tumorigenesis, from (stem) cell transformation to tumor escape. In this context, BMPs (Bone Morphogenetic Proteins), are key mediators of stem cell regulation in both embryonic and adult organs such as hematopoietic, neural and epithelial tissues. BMPs directly regulate the niche and stem cells residing within. Among them, BMP2 and BMP4 emerged as master regulators of normal and tumorigenic processes. Recently, a number of studies unraveled important mechanisms that sustain cell transformation related to dysregulations of the BMP pathway in stem cells and their niche (including exposure to pollutants such as bisphenols). Furthermore, a direct link between BMP2/BMP4 binding to BMP type 1 receptors and the emergence and expansion of cancer stem cells was unveiled. In addition, a chronic exposure of normal stem cells to abnormal BMP signals contributes to the emergence of cancer stem cells, or to disease progression independently of the initial transforming event. In this review, we will illustrate how the regulation of stem cells and their microenvironment becomes dysfunctional in cancer via the hijacking of BMP signaling with main examples in myeloid leukemia and breast cancers.
Keywords: BMP; bisphenol; cancer; environmental exposure; mesenchymal; microenvironment; resistance; stem cells.
Copyright © 2022 Guyot, Lefort, Voeltzel, Pécheur and Maguer-Satta.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

