Exercise-Induced Bronchoconstriction in Children
- PMID: 35047536
- PMCID: PMC8761949
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.814976
Exercise-Induced Bronchoconstriction in Children
Abstract
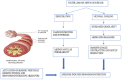
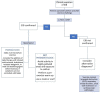
Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction (EIB) is a transient airflow obstruction, typically 5-15 min after physical activity. The pathophysiology of EIB is related to the thermal and osmotic changes of the bronchial mucosa, which cause the release of mediators and the development of bronchoconstriction in the airways. EIB in children often causes an important limitation to physical activities and sports. However, by taking appropriate precautions and through adequate pharmacological control of the condition, routine exercise is extremely safe in children. This review aims to raise awareness of EIB by proposing an update, based on the latest studies, on pathological mechanisms, diagnosis, and therapeutic approaches in children.
Keywords: asthma; atopy; children; exercise induced asthma; exercise-induced bronchoconstriction.
Copyright © 2022 Klain, Indolfi, Dinardo, Contieri, Decimo and Miraglia Del Giudice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- ACAAI Public Website. Exercise-Induced Bronchoconstriction (EIB) . (2021). Available online at: https://acaai.org/asthma/types-of-asthma/exercise-induced-bronchoconstri.... (accessed November 29, 2021).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources