Temperature Dependence of Water Contact Angle on Teflon AF1600
- PMID: 35048705
- PMCID: PMC8812120
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.1c03202
Temperature Dependence of Water Contact Angle on Teflon AF1600
Abstract
In this work, we investigate the change of contact angle (CA) of a water droplet during evaporation on a Teflon AF1600 surface in the temperature range between 20 and 80 °C under standard laboratory conditions. An almost constant initial CA and a significant increase of the stabilized CA have been observed. The results reveal a temperature-dependent CA change, mainly due to water adsorption on the solid surface. Soaking experiments indicate that besides adsorption, a temperature-independent friction-like force contributes to the pinning of triple-line and therefore to the CA change. We propose an adsorption coverage parameter and a friction-like force to describe the CA change. Furthermore, we describe a reproducible process to produce smooth and homogeneous Teflon AF1600 thin films, minimizing the influence of roughness and local heterogeneity on the CA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
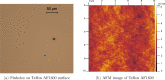
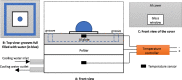

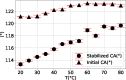
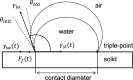
References
-
- Young T. III. An essay on the cohesion of fluids. Philosophical transactions of the royal society of London 1805, 65–87.
-
- Wadhai S. M.; Sawane Y. B.; Banpurkar A. G. Electrowetting behaviour of thermostable liquid over wide temperature range. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 2365–2371. 10.1007/s10853-019-04120-4. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

