Characterisation of age and polarity at onset in bipolar disorder
- PMID: 35048876
- PMCID: PMC8636611
- DOI: 10.1192/bjp.2021.102
Characterisation of age and polarity at onset in bipolar disorder
Abstract
Background: Studying phenotypic and genetic characteristics of age at onset (AAO) and polarity at onset (PAO) in bipolar disorder can provide new insights into disease pathology and facilitate the development of screening tools.
Aims: To examine the genetic architecture of AAO and PAO and their association with bipolar disorder disease characteristics.
Method: Genome-wide association studies (GWASs) and polygenic score (PGS) analyses of AAO (n = 12 977) and PAO (n = 6773) were conducted in patients with bipolar disorder from 34 cohorts and a replication sample (n = 2237). The association of onset with disease characteristics was investigated in two of these cohorts.
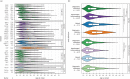
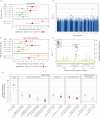
Results: Earlier AAO was associated with a higher probability of psychotic symptoms, suicidality, lower educational attainment, not living together and fewer episodes. Depressive onset correlated with suicidality and manic onset correlated with delusions and manic episodes. Systematic differences in AAO between cohorts and continents of origin were observed. This was also reflected in single-nucleotide variant-based heritability estimates, with higher heritabilities for stricter onset definitions. Increased PGS for autism spectrum disorder (β = -0.34 years, s.e. = 0.08), major depression (β = -0.34 years, s.e. = 0.08), schizophrenia (β = -0.39 years, s.e. = 0.08), and educational attainment (β = -0.31 years, s.e. = 0.08) were associated with an earlier AAO. The AAO GWAS identified one significant locus, but this finding did not replicate. Neither GWAS nor PGS analyses yielded significant associations with PAO.
Conclusions: AAO and PAO are associated with indicators of bipolar disorder severity. Individuals with an earlier onset show an increased polygenic liability for a broad spectrum of psychiatric traits. Systematic differences in AAO across cohorts, continents and phenotype definitions introduce significant heterogeneity, affecting analyses.
Keywords: Bipolar disorder; GWAS; age at onset; polarity at onset; polygenic score.
Conflict of interest statement
Amare T. Azmeraw: has received 2020–2022 NARSAD Young Investigator Grant from the Brain & Behaviour Research Foundation. Ole A. Andreassen: speaker's honorarium Sunovion, Lundbeck. Consultant HealthLytix. Bernhard Baune: Honoraria: Lundbeck, Janssen, LivaNova, Servier. Carrie Bearden: Novartis Scientific Advisory Board. Clark Scott: Honoraria and Investigator-initiated project funding from Jannsen-Cilag Australia, Lundbeck-Otsuka Australia. J. Raymond DePaulo: owns stock in CVS Health; JRD was unpaid consultant for Myriad Neuroscience 2017 & 2019. Michael C. O´Donovan: research unrelated to this manuscript supported by a collaborative research grant from Takeda Pharmaceuticals. Bruno Etain: honoraria for Sanofi. Mark A. Frye: grant Support Assurex Health, Mayo Foundation, Medibio Consultant (Mayo) Actify Neurotherapies, Allergan, Intra-Cellular Therapies, Inc., Janssen, Myriad, Neuralstem Inc., Sanofi, Takeda, Teva Pharmaceuticals. Per Hoffmann: employee of Life&Brain GmbH, Member of the Scientific Advisory Board of HMG Systems Engeneering GmbH. Mikael Landen: Speaker's honoraria Lundbeck pharmaceuticals. Andrew M McIntosh: research funding from The Sackler Trust, speaker fees from Illumina and Janssen. Philip B. Mitchell: remuneration for lectures in China on bipolar disorder research by Sanofi (Hangzhou). John Nurnberger: investigator for Janssen. Benjamin M. Neale: is a member of the scientific advisory board at Deep Genomics and RBNC Therapeutics. A consultant for Camp4 Therapeutics, Takeda Pharmaceutical and Biogen. Andreas Reif: apeaker's honoraria / Advisory boards: Janssen, Shire/Takeda, Medice, SAGE and Servier. Eli Stahl: now employed by the Regeneron Genetics Center. Kato Tadafumi: honoraria: Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., GlaxoSmithKline K.K., Taisho Pharma Co., Ltd., Taisho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Taisho Toyama Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma Co., Ltd., Meiji Seika Pharma Co., Ltd., Pfizer Japan Inc., Mochida Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Shionogi & Co., Ltd., Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., Janssen Asia Pacific, Yoshitomiyakuhin, Astellas Pharma Inc., Nippon, Boehringer Ingelheim Co. Ltd., MSD K.K., Kyowa Pharmaceutical Industry Co., Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Eisai Co., Ltd. Grants: Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma Co., Ltd., Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Shionogi & Co., Ltd., Eisai Co., Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation. Thomas G. Schulze: is a member of the editorial board of
Figures
References
-
- Cloutier M, Greene M, Guerin A, Touya M, Wu E. The economic burden of bipolar I disorder in the United States in 2015. J Affect Disord 2018; 226: 45–51. - PubMed
-
- Berk M, Dodd S, Callaly P, Berk L, Fitzgerald P, de Castella AR, et al. History of illness prior to a diagnosis of bipolar disorder or schizoaffective disorder. J Affect Disord 2007. Nov; 103: 181–6. - PubMed

