Internal senses of the vagus nerve
- PMID: 35051375
- PMCID: PMC8857038
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2021.12.020
Internal senses of the vagus nerve
Abstract
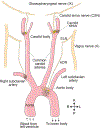
The vagus nerve is an indispensable body-brain connection that controls vital aspects of autonomic physiology like breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, and gut motility, reflexes like coughing and swallowing, and survival behaviors like feeding, drinking, and sickness responses. Classical physiological studies and recent molecular/genetic approaches have revealed a tremendous diversity of vagal sensory neuron types that innervate different internal organs, with many cell types remaining poorly understood. Here, we review the state of knowledge related to vagal sensory neurons that innervate the respiratory, cardiovascular, and digestive systems. We focus on cell types and their response properties, physiological/behavioral roles, engaged neural circuits and, when possible, sensory receptors. We are only beginning to understand the signal transduction mechanisms used by vagal sensory neurons and upstream sentinel cells, and future studies are needed to advance the field of interoception to the level of mechanistic understanding previously achieved for our external senses.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests S.D.L. is a consultant for Kallyope.
Figures

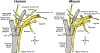
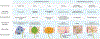
References
-
- Abdulqawi R, Dockry R, Holt K, Layton G, McCarthy BG, Ford AP, and Smith JA (2015). P2X3 receptor antagonist (AF-219) in refractory chronic cough: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 study. Lancet 385, 1198–1205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

