COVID-19-induced pulmonary sarcoid: A case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 35051738
- PMCID: PMC8755635
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2021.12.021
COVID-19-induced pulmonary sarcoid: A case report and review of the literature
Abstract
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in dramatic loss of life worldwide, but as the large number of acutely ill patients subsides, the emerging group of "COVID-19 long-haulers" present a clinical challenge. Studies have shown that many of these patients suffer long-term pulmonary disease related to residual fibrosis. Prior studies have shown that while many patients have non-specific findings of fibrotic-like changes, others develop specific patterns of interstitial lung disease.
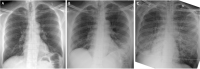
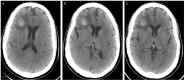
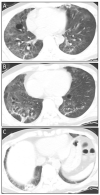
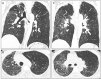
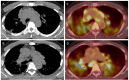
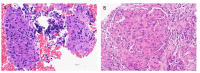
Case report: Here, we present the first case of a patient developing pulmonary sarcoidosis one year after critical illness from COVID-19. He developed numerous non-necrotizing and well-formed granulomas in mediastinal lymph nodes and pulmonary nodules, compatible radiographically and pathologically with sarcoid.
Conclusions: While the pathophysiology of sarcoid is incompletely understood, inflammation is mediated through the dysregulation of a number of different cytokines (IFNγ, IL-2, IL-12, IL-17, IL-22). This case provides valuable clues for better understanding of the shared pathophysiology of cytokine dysregulation seen in COVID-19 and other interstitial lung diseases such as sarcoidosis.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cardiothoracic; Cytokine; Interstitial lung disease; Sarcoid.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Mary M. Salvatore- Speaker and Consultant: Genentech, Boehringer Ingelheim. Grant funding: Genentech, Boehringer Ingelheim.
Figures
References
-
- Baig A.M. Deleterious outcomes in long-hauler COVID-19: the effects of SARS-CoV-2 on the CNS in chronic COVID syndrome. ACS Chem Nerosci. 2020;11(24):4017–4020. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

