Neutralizing antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron variants following heterologous CoronaVac plus BNT162b2 booster vaccination
- PMID: 35051990
- PMCID: PMC8938264
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-022-01705-6
Neutralizing antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron variants following heterologous CoronaVac plus BNT162b2 booster vaccination
Abstract
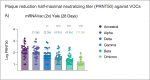
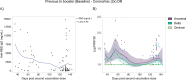
The recent emergence of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant is raising concerns because of its increased transmissibility and its numerous spike mutations, which have the potential to evade neutralizing antibodies elicited by COVID-19 vaccines. Here we evaluated the effects of a heterologous BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine booster on the humoral immunity of participants who had received a two-dose regimen of CoronaVac, an inactivated vaccine used globally. We found that a heterologous CoronaVac prime vaccination of two doses followed by a BNT162b2 booster induces elevated virus-specific antibody levels and potent neutralization activity against the ancestral virus and the Delta variant, resembling the titers obtained after two doses of mRNA vaccines. Although neutralization of Omicron was undetectable in participants who had received a two-dose regimen of CoronaVac, the BNT162b2 booster resulted in a 1.4-fold increase in neutralization activity against Omicron compared with the two-dose mRNA vaccine. Despite this increase, neutralizing antibody titers were reduced by 7.1-fold and 3.6-fold for Omicron compared with the ancestral strain and the Delta variant, respectively. These findings have immediate implications for multiple countries that previously used a CoronaVac regimen and reinforce the idea that the Omicron variant is associated with immune escape from vaccines or infection-induced immunity, highlighting the global need for vaccine boosters to combat the impact of emerging variants.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A.I. served as a consultant for RIGImmune, Xanadu and Revelar Biotherapeutics. I.Y. reported being a member of the mRNA-1273 Study Group and has received funding to her institution to conduct clinical research from BioFire, MedImmune, Regeneron, PaxVax, Pfizer, GSK, Merck, Novavax, Sanofi-Pasteur and Micron. N.D.G. is a consultant for Tempus Labs to develop infectious disease diagnostic assays. A.I.K. serves as an expert panel member for Reckitt Global Hygiene Institute, a scientific advisory board member for Revelar Biotherapeutics and a consultant for Tata Medical and Diagnostics and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, and has received grants from Merck, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, and Tata Medical and Diagnostics for research related to COVID-19 outside of the submitted work. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Pulliam, J. R. C. et al. Increased risk of SARS-CoV-2 reinfection associated with emergence of the Omicron variant in South Africa. Preprint at medRxiv10.1101/2021.11.11.21266068 (2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

