Influence of Haptoglobin Polymorphism on Stroke in Sickle Cell Disease Patients
- PMID: 35052484
- PMCID: PMC8775574
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13010144
Influence of Haptoglobin Polymorphism on Stroke in Sickle Cell Disease Patients
Abstract
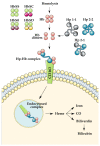
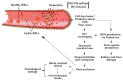
This review outlines the current clinical research investigating how the haptoglobin (Hp) genetic polymorphism and stroke occurrence are implicated in sickle cell disease (SCD) pathophysiology. Hp is a blood serum glycoprotein responsible for binding and removing toxic free hemoglobin from the vasculature. The role of Hp in patients with SCD is critical in combating blood toxicity, inflammation, oxidative stress, and even stroke. Ischemic stroke occurs when a blocked vessel decreases oxygen delivery in the blood to cerebral tissue and is commonly associated with SCD. Due to the malformed red blood cells of sickle hemoglobin S, blockage of blood flow is much more prevalent in patients with SCD. This review is the first to evaluate the role of the Hp polymorphism in the incidence of stroke in patients with SCD. Overall, the data compiled in this review suggest that further studies should be conducted to reveal and evaluate potential clinical advancements for gene therapy and Hp infusions.
Keywords: brain ischemia; genotype; hemolytic anemia; hospitalization; inflammation; mini-stroke; oxidative stress; pain crisis; silent cerebral infarction; therapy; vaso-occlusion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Piel F.B., Patil A.P., Howes R.E., Nyangiri O.A., Gething P.W., Dewi M., Temperley W.H., Williams T.N., Weatherall D.J., Hay S.I. Global epidemiology of sickle haemoglobin in neonates: A contemporary geostatistical model-based map and population estimates. Lancet. 2013;381:142–151. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61229-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sedrak A., Kondamudi N.P. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2021. Sickle Cell Disease. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

