Implications of Vitamins in COVID-19 Prevention and Treatment through Immunomodulatory and Anti-Oxidative Mechanisms
- PMID: 35052509
- PMCID: PMC8773198
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11010005
Implications of Vitamins in COVID-19 Prevention and Treatment through Immunomodulatory and Anti-Oxidative Mechanisms
Abstract
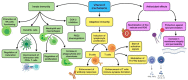
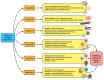
Since the appearance of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and its announcement as a global pandemic, the search for prophylactic and therapeutic options have become a priority for governments and the scientific community. The approval of several vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 is being crucial to overcome this situation, although the victory will not be achieved while the whole population worldwide is not protected against the virus. This is why alternatives should be studied in order to successfully support the immune system before and during a possible infection. An optimal inflammatory and oxidative stress status depends on an adequate diet. Poor levels of several nutrients could be related to an impaired immune response and, therefore, an increased susceptibility to infection and serious outcomes. Vitamins exert a number of anti-microbial, immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant activities, which can be of use to fight against this and several other diseases (especially vitamin D and C). Even though they cannot be considered as a definitive therapeutic option, in part owing to the lack of solid conclusions from well-designed clinical trials, currently available evidence from similar respiratory diseases may indicate that it would be rational to deeply explore the use of vitamins during this global pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; immunity; inflammation; nutrients; oxidative stress; vitamins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

