Evaluation of Heterocyclic Carboxamides as Potential Efflux Pump Inhibitors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 35052908
- PMCID: PMC8772707
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics11010030
Evaluation of Heterocyclic Carboxamides as Potential Efflux Pump Inhibitors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
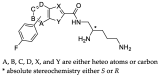
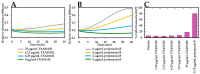
The ability to rescue the activity of antimicrobials that are no longer effective against bacterial pathogens such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an attractive strategy to combat antimicrobial drug resistance. Herein, novel efflux pump inhibitors (EPIs) demonstrating strong potentiation in combination with levofloxacin against wild-type P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 are presented. A structure activity relationship of aryl substituted heterocyclic carboxamides containing a pentane diamine side chain is described. Out of several classes of fused heterocyclic carboxamides, aryl indole carboxamide compound 6j (TXA01182) at 6.25 µg/mL showed 8-fold potentiation of levofloxacin. TXA01182 was found to have equally synergistic activities with other antimicrobial classes (monobactam, fluoroquinolones, sulfonamide and tetracyclines) against P. aeruginosa. Several biophysical and genetic studies rule out membrane disruption and support efflux inhibition as the mechanism of action (MOA) of TXA01182. TXA01182 was determined to lower the frequency of resistance (FoR) of the partner antimicrobials and enhance the killing kinetics of levofloxacin. Furthermore, TXA01182 demonstrated a synergistic effect with levofloxacin against several multidrug resistant P. aeruginosa clinical isolates.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; RND efflux pumps; antimicrobial drug resistance; efflux pump inhibitors; heterocyclic carboxamides.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors are associated with TAXIS Pharmaceuticals Inc. and thus declare conflict of interest.
Figures
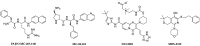
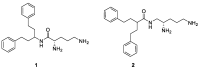

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of a Conformationally Constrained Indole Carboxamide as a Potential Efflux Pump Inhibitor in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 May 26;11(6):716. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11060716. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35740123 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of inhibitors of multidrug resistance efflux pumps in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: novel agents for combination therapy.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001 Jan;45(1):105-16. doi: 10.1128/AAC.45.1.105-116.2001. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001. PMID: 11120952 Free PMC article.
-
Conessine as a novel inhibitor of multidrug efflux pump systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Aug 14;17(1):405. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1913-y. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28806947 Free PMC article.
-
[The role of cell wall organization and active efflux pump systems in multidrug resistance of bacteria].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2007 Apr;41(2):309-27. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2007. PMID: 17682720 Review. Turkish.
-
Recent advances toward a molecular mechanism of efflux pump inhibition.Front Microbiol. 2015 May 5;6:421. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00421. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25999939 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial and Anti-Efflux Machinery of FDA-Approved Proton Pump Inhibitors and Vitamins Against Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Microorganisms. 2025 May 27;13(6):1227. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13061227. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40572115 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic potentiators as a promising strategy for combating antibiotic resistance.NPJ Antimicrob Resist. 2025 Jun 6;3(1):53. doi: 10.1038/s44259-025-00112-4. NPJ Antimicrob Resist. 2025. PMID: 40481260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Structures and Binding Modes of Small-Molecule Inhibitors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Elastase LasB.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Aug 4;11(8):1060. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11081060. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36009930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Update on the Discovery of Efflux Pump Inhibitors against Critical Priority Gram-Negative Bacteria.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Jan 15;12(1):180. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12010180. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36671381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial Efflux Pump Inhibitors Reduce Antibiotic Resistance.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jan 25;16(2):170. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16020170. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38399231 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

