Human Sensory Neuron-like Cells and Glycated Collagen Matrix as a Model for the Screening of Analgesic Compounds
- PMID: 35053363
- PMCID: PMC8773477
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11020247
Human Sensory Neuron-like Cells and Glycated Collagen Matrix as a Model for the Screening of Analgesic Compounds
Erratum in
-
Correction: Bufalo et al. Human Sensory Neuron-like Cells and Glycated Collagen Matrix as a Model for the Screening of Analgesic Compounds. Cells 2022, 11, 247.Cells. 2024 Jun 24;13(13):1089. doi: 10.3390/cells13131089. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38995017 Free PMC article.
Abstract
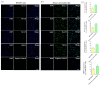
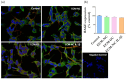
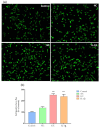
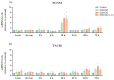
Increased collagen-derived advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) are consistently related to painful diseases, including osteoarthritis, diabetic neuropathy, and neurodegenerative disorders. We have recently developed a model combining a two-dimensional glycated extracellular matrix (ECM-GC) and primary dorsal root ganglion (DRG) that mimicked a pro-nociceptive microenvironment. However, culturing primary cells is still a challenge for large-scale screening studies. Here, we characterized a new model using ECM-GC as a stimulus for human sensory-like neurons differentiated from SH-SY5Y cell lines to screen for analgesic compounds. First, we confirmed that the differentiation process induces the expression of neuron markers (MAP2, RBFOX3 (NeuN), and TUBB3 (β-III tubulin), as well as sensory neuron markers critical for pain sensation (TRPV1, SCN9A (Nav1.7), SCN10A (Nav1.8), and SCN11A (Nav1.9). Next, we showed that ECM-GC increased c-Fos expression in human sensory-like neurons, which is suggestive of neuronal activation. In addition, ECM-GC upregulated the expression of critical genes involved in pain, including SCN9A and TACR1. Of interest, ECM-GC induced substance P release, a neuropeptide widely involved in neuroinflammation and pain. Finally, morphine, the prototype opiate, decreased ECM-GC-induced substance P release. Together, our results suggest that we established a functional model that can be useful as a platform for screening candidates for the management of painful conditions.
Keywords: analgesic compounds; high-content screening; in vitro assays; inflammatory disease; nociception; two-dimensional culture.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

