Gastrointestinal Adenocarcinoma Incidence and Survival Trends in South Australia, 1990-2017
- PMID: 35053439
- PMCID: PMC8773524
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14020275
Gastrointestinal Adenocarcinoma Incidence and Survival Trends in South Australia, 1990-2017
Abstract
Background & aims: Globally, there has been a concerning rise in the incidence of young-onset cancers. The aim of this study was to provide trends in the incidence and survival of gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas (oesophagus, stomach, pancreas, and colorectal) in South Australia over a 27-year period.
Methods: This is a cross-sectional analysis of a prospective longitudinal database including all cases of gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas prospectively reported to the South Australian (State) Cancer Registry from 1990 to 2017.
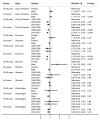
Results: A total of 28,566 patients diagnosed with oesophageal, stomach, pancreatic, or colorectal adenocarcinoma between 1990 and 2017 were included in the study. While the overall incidence for gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas in individuals >50 years has decreased since 2000 (IRR of 0.97 (95% CI 0.94-1.00; p = 0.06)) compared to 1990-1999, the rate amongst individuals aged 18-50 has significantly increased (IRR 1.41 (95% CI 1.27-1.57; p < 0.001)) during the same reference time period. Although noted in both sexes, the rate of increase in incidence was significantly greater in males (11.5 to 19.7/100,000; p < 0.001). The overall survival from adenocarcinomas across all subsites improved in the >50-year cohort in the last decade (HR 0.89 (95% CI 0.86-0.93; p < 0.001)) compared to 1990-1999. In individuals aged 18-50 years, there has only been a significant improvement in survival for colorectal cancer (HR 0.82 (95% CI 0.68-0.99; p < 0.04)), but not the other subsites. A lower overall survival was noted for males in both age cohorts (18-50 years-HR 1.24 (95% CI 1.09-1.13; p < 0.01) and >50 years-HR 1.13 (95% CI 1.10-1.16; p < 0.001), respectively) compared to females.
Conclusions: This study from South Australia demonstrates a significant increase in young-onset gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas over the last 28 years, with a greater increase in the male sex. The only significant improvement in survival in this cohort has been noted in colorectal cancer patients.
Keywords: colon; morbidity; mortality; outcomes; pancreas; stomach.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- McWilliams R.R., Maisonneuve P., Bamlet W.R., Petersen G.M., Li D., Risch H.A., Yu H., Fontham E.T., Luckett B., Bosetti C., et al. Risk Factors for Early-Onset and Very-Early-Onset Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: A Pancreatic Cancer Case-Control Consortium (Panc4) Analysis. Pancreas. 2016;45:311–316. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000392. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

