Immunotherapy and Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Review of New Treatment Approaches
- PMID: 35054417
- PMCID: PMC8781308
- DOI: 10.3390/life12010024
Immunotherapy and Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Review of New Treatment Approaches
Abstract
Introduction: Renal cell carcinomas (RCC) have been treated with immunotherapy for decades; the use of immune checkpoint inhibitors represents the most recent advance. In this review, we compare these new RCC immunotherapies, with a focus on achieving durable complete responses (CR).
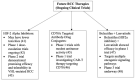
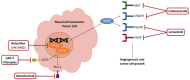
Review: Sorafenib and sunitinib were the first Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved targeted agents for RCC, with sunitinib eventually becoming the standard-of-care agent against which novel therapies are compared. In the last five years, many combination therapies based on the use of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) and receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), including ipilimumab/nivolumab, nivolumab/cabozantinib, avelumab/axitinib, pembrolizumab/axitinib, and pembrolizumab/lenvatinib, have demonstrated superior overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) compared to sunitinib. Ongoing clinical trials of hypoxia-induced factor-2 alpha (HIF-2a) inhibitors, chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CAR-T) therapy targeting CD70, and other new combination therapies have also shown promise and are currently under investigation.
Conclusions: Many new combination therapies are approved for RCC treatment, and CR rates suggest that, in the era of immunotherapy, it may be possible to achieve durable responses and survival benefit in patients with metastatic RCC.
Keywords: complete response rate; immune checkpoint inhibitors; immunotherapy; renal cell carcinoma; sunitinib.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cancer of the Kidney and Renal Pelvis—Cancer Stat Facts SEER. [(accessed on 30 August 2021)]; Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/kidrp.html.
-
- Negrier S., Escudier B., Lasset C., Douillard J.-Y., Savary J., Chevreau C., Ravaud A., Mercatello A., Peny J., Mousseau M., et al. Recombinant Human Interleukin-2, Recombinant Human Interferon Alfa-2a, or Both in Metastatic Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998;338:1272–1278. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199804303381805. - DOI - PubMed
-
- McDermott D.F., Regan M.M., Clark J.I., Flaherty L.E., Weiss G.R., Logan T.F., Kirkwood J.M., Gordon M.S., Sosman J.A., Ernstoff M.S., et al. Randomized Phase III Trial of High-Dose Interleukin-2 Versus Subcutaneous Interleukin-2 and Interferon in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005;23:133–141. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.03.206. - DOI - PubMed
-
- McDermott D.F., Cheng S.-C., Signoretti S., Margolin K., Clark J.I., Sosman J.A., Dutcher J.P., Logan T.F., Curti B.D., Ernstoff M.S., et al. The High-Dose Aldesleukin “Select” Trial: A Trial to Prospectively Validate Predictive Models of Response to Treatment in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015;21:561–568. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-1520. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials