Multifunctional Membranes-A Versatile Approach for Emerging Pollutants Removal
- PMID: 35054593
- PMCID: PMC8778428
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes12010067
Multifunctional Membranes-A Versatile Approach for Emerging Pollutants Removal
Abstract
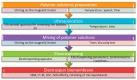
This paper presents a comprehensive literature review surveying the most important polymer materials used for electrospinning processes and applied as membranes for the removal of emerging pollutants. Two types of processes integrate these membrane types: separation processes, where electrospun polymers act as a support for thin film composites (TFC), and adsorption as single or coupled processes (photo-catalysis, advanced oxidation, electrochemical), where a functionalization step is essential for the electrospun polymer to improve its properties. Emerging pollutants (EPs) released in the environment can be efficiently removed from water systems using electrospun membranes. The relevant results regarding removal efficiency, adsorption capacity, and the size and porosity of the membranes and fibers used for different EPs are described in detail.
Keywords: electrospinning; emerging pollutants; membranes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sakib M.N., Mallik A.K., Rahman M.M. Update on chitosan-based electrospun nanofibers for wastewater treatment: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2021;2:100064. doi: 10.1016/j.carpta.2021.100064. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources