Neuroinflammation: A Potential Risk for Dementia
- PMID: 35054805
- PMCID: PMC8775769
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23020616
Neuroinflammation: A Potential Risk for Dementia
Abstract
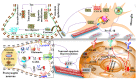
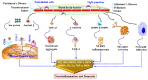
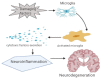
Dementia is a neurodegenerative condition that is considered a major factor contributing to cognitive decline that reduces independent function. Pathophysiological pathways are not well defined for neurodegenerative diseases such as dementia; however, published evidence has shown the role of numerous inflammatory processes in the brain contributing toward their pathology. Microglia of the central nervous system (CNS) are the principal components of the brain's immune defence system and can detect harmful or external pathogens. When stimulated, the cells trigger neuroinflammatory responses by releasing proinflammatory chemokines, cytokines, reactive oxygen species, and nitrogen species in order to preserve the cell's microenvironment. These proinflammatory markers include cytokines such as IL-1, IL-6, and TNFα chemokines such as CCR3 and CCL2 and CCR5. Microglial cells may produce a prolonged inflammatory response that, in some circumstances, is indicated in the promotion of neurodegenerative diseases. The present review is focused on the involvement of microglial cell activation throughout neurodegenerative conditions and the link between neuroinflammatory processes and dementia.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; chemokines; cytokines; dementia; microglial cell activation; neuroinflammation; phagocytosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- United Nations . World Population Ageing 2019. Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division; New York, NY, USA: 2019. pp. 1–111.
-
- Rahman M., Bajgai J., Fadriquela A., Sharma S., Trinh Thi T., Akter R., Goh S.H., Kim C.-S., Lee K.-J. Redox Effects of Molecular Hydrogen and Its Therapeutic Efficacy in the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Processes. 2021;9:308. doi: 10.3390/pr9020308. - DOI
-
- Australia D., Baker S., Banerjee S. World Alzheimer Report 2019: Attitudes to Dementia. Alzheimer’s Disease International; London, UK: 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

