Cancer Stem Cells and Their Vesicles, Together with Other Stem and Non-Stem Cells, Govern Critical Cancer Processes: Perspectives for Medical Development
- PMID: 35054811
- PMCID: PMC8775347
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23020625
Cancer Stem Cells and Their Vesicles, Together with Other Stem and Non-Stem Cells, Govern Critical Cancer Processes: Perspectives for Medical Development
Abstract
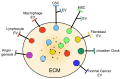
Stem cells, identified several decades ago, started to attract interest at the end of the nineties when families of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), concentrated in the stroma of most organs, were found to participate in the therapy of many diseases. In cancer, however, stem cells of high importance are specific to another family, the cancer stem cells (CSCs). This comprehensive review is focused on the role and the mechanisms of CSCs and of their specific extracellular vesicles (EVs), which are composed of both exosomes and ectosomes. Compared to non-stem (normal) cancer cells, CSCs exist in small populations that are preferentially distributed to the niches, such as minor specific tissue sites corresponding to the stroma of non-cancer tissues. At niches and marginal sites of other cancer masses, the tissue exhibits peculiar properties that are typical of the tumor microenvironment (TME) of cancers. The extracellular matrix (ECM) includes components different from non-cancer tissues. CSCs and their EVs, in addition to effects analogous to those of MSCs/EVs, participate in processes of key importance, specific to cancer: generation of distinct cell subtypes, proliferation, differentiation, progression, formation of metastases, immune and therapy resistance, cancer relapse. Many of these, and other, effects require CSC cooperation with surrounding cells, especially MSCs. Filtered non-cancer cells, especially macrophages and fibroblasts, contribute to collaborative cancer transition/integration processes. Therapy developments are mentioned as ongoing preclinical initiatives. The preliminary state of clinical medicine is presented in terms of both industrial development and future treatments. The latter will be administered to specific patients together with known drugs, with the aim of eradicating their tumor growth and metastases.
Keywords: cancer differentiation; cancer progression and relapse; cancer stem cells; clinical medicine; extracellular vesicles; mesenchymal stem cells; metastasis; niches; non-stem cancer cells; normal; therapy; tumoral microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Extracellular Vesicles and Cancer Stem Cells in Tumor Progression: New Therapeutic Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 29;22(19):10572. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910572. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Concise Review: Cancer Cells, Cancer Stem Cells, and Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Influence in Cancer Development.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017 Dec;6(12):2115-2125. doi: 10.1002/sctm.17-0138. Epub 2017 Oct 26. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 29072369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of mesenchymal stem cells in cancer progression and metastases.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2015;15(2):88-98. doi: 10.2174/1568009615666150126154151. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2015. PMID: 25619387 Review.
-
Modulatory effects of cancer stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles on the tumor immune microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 19;15:1362120. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1362120. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38962016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles from human liver stem cells inhibit renal cancer stem cell-derived tumor growth in vitro and in vivo.Int J Cancer. 2020 Sep 15;147(6):1694-1706. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32925. Epub 2020 Feb 25. Int J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32064610 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles and Study of Their Inhibitory Effect on Bulk Cancer Cells and Cancer Stem Cells in Breast Carcinoma.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Sep 24;12(19):3324. doi: 10.3390/nano12193324. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36234451 Free PMC article.
-
A Green Synthesis of Au-Ag Alloy Nanoparticles using Polydopamine Chemistry: Evaluation of their Anticancer Potency Towards Both MCF-7 Cells and their Cancer Stem Cells Subgroup.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2024;24(13):969-981. doi: 10.2174/0118715206296123240331050206. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38616743
-
Unconventional protein secretion (UPS): role in important diseases.Mol Biomed. 2023 Jan 9;4(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s43556-022-00113-z. Mol Biomed. 2023. PMID: 36622461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Four distinct cytoplasmic structures generate and release specific vesicles, thus opening the way to intercellular communication.Extracell Vesicles Circ Nucl Acids. 2023 Mar 15;4(1):44-58. doi: 10.20517/evcna.2023.03. eCollection 2023. Extracell Vesicles Circ Nucl Acids. 2023. PMID: 39698300 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

