CD44, γ-H2AX, and p-ATM Expressions in Short-Term Ex Vivo Culture of Tumour Slices Predict the Treatment Response in Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 35055060
- PMCID: PMC8775909
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23020877
CD44, γ-H2AX, and p-ATM Expressions in Short-Term Ex Vivo Culture of Tumour Slices Predict the Treatment Response in Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
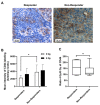
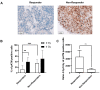
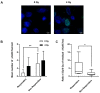
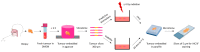
Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common type of head and neck cancer (HNSCC) with a disease-free survival at 3 years that does not exceed 30%. Biomarkers able to predict clinical outcomes are clearly needed. The purpose of this study was to investigate whether a short-term culture of tumour fragments irradiated ex vivo could anticipate patient responses to chemo- and/or radiotherapies. Biopsies were collected prior to treatment from a cohort of 28 patients with non-operable tumours of the oral cavity or oropharynx, and then cultured ex vivo. Short-term biopsy slice culture is a robust method that keeps cells viable for 7 days. Different biomarkers involved in the stemness status (CD44) or the DNA damage response (pATM and γ-H2AX) were investigated for their potential to predict the treatment response. A higher expression of all these markers was predictive of a poor response to treatment. This allowed the stratification of responder or non-responder patients to treatment. Moreover, the ratio for the expression of the three markers 24 h after 4 Gy irradiation versus 0 Gy was higher in responder than in non-responder patients. Finally, combining these biomarkers greatly improved their predictive potential, especially when the γ-H2AX ratio was associated with the CD44 ratio or the pATM ratio. These results encourage further evaluation of these biomarkers in a larger cohort of patients.
Keywords: CD44; DNA damage response; HNSCC; ex vivo culture; pATM; predictive biomarker; γ-H2AX foci.
Conflict of interest statement
G.M. and S.S. are employed by the LXRepair Company (La Tronche, France). The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Tinhofer I., Stenzinger A., Eder T., Konschak R., Niehr F., Endris V., Distel L., Hautmann M.G., Mandic R., Stromberger C., et al. Targeted next-generation sequencing identifies molecular subgroups in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck with distinct outcome after concurrent chemoradiation. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2016;27:2262–2268. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw426. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Linge A., Lohaus F., Löck S., Nowak A., Gudziol V., Valentini C., von Neubeck C., Jütz M., Tinhofer I., Budach V., et al. HPV status, cancer stem cell marker expression, hypoxia gene signatures and tumour volume identify good prognosis subgroups in patients with HNSCC after primary radiochemotherapy: A multicentre retrospective study of the german cancer consortium radiation oncology group (DKTK-ROG) Radiother. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 2016;121:364–373. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2016.11.008. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

