Biphasic Functions of Sodium Fluoride (NaF) in Soft and in Hard Periodontal Tissues
- PMID: 35055148
- PMCID: PMC8780524
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23020962
Biphasic Functions of Sodium Fluoride (NaF) in Soft and in Hard Periodontal Tissues
Abstract
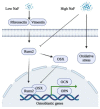
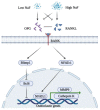
Sodium fluoride (NaF) is widely used in clinical dentistry. However, the administration of high or low concentrations of NaF has various functions in different tissues. Understanding the mechanisms of the different effects of NaF will help to optimize its use in clinical applications. Studies of NaF and epithelial cells, osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and periodontal cells have suggested the significant roles of fluoride treatment. In this review, we summarize recent studies on the biphasic functions of NaF that are related to both soft and hard periodontal tissues, multiple diseases, and clinical dentistry.
Keywords: epithelial cells; fluoride; mesenchymal stem cells; miRNA; osteoblasts; osteoclasts; periodontal disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sodium fluoride induces hypercalcemia resulting from the upregulation of both osteoblastic and osteoclastic activities in goldfish, Carassius auratus.Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2016 Nov;189:54-60. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2016.07.006. Epub 2016 Jul 27. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27475026
-
Differential effects of fluoride during osteoblasts mineralization in C57BL/6J and C3H/HeJ inbred strains of mice.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2014 Oct;161(1):123-9. doi: 10.1007/s12011-014-0086-5. Epub 2014 Jul 31. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2014. PMID: 25074429
-
Fluoride increases rat osteoblast function and population after in vivo administration but not after in vitro exposure.Bone. 1993 Sep-Oct;14(5):721-5. doi: 10.1016/8756-3282(93)90203-m. Bone. 1993. PMID: 8268046
-
Anabolic effects of fluoride on bone.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 1995 Sep;6(7):229-34. doi: 10.1016/1043-2760(95)00111-t. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 1995. PMID: 11540313 Review.
-
Sodium fluoride therapy of postmenopausal osteoporosis.Endocr Rev. 1993 Jun;14(3):312-23. doi: 10.1210/edrv-14-3-312. Endocr Rev. 1993. PMID: 8319597 Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive in vitro and in ovo assessment of cytotoxicity: Unraveling the impact of sodium fluoride, xylitol, and their synergistic associations in dental products.Biomol Biomed. 2024 Mar 2;24(4):923-938. doi: 10.17305/bb.2024.10181. Biomol Biomed. 2024. PMID: 38431834 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Sodium Fluoride Mouthwash in Regulating FGF-2 and TGF-β Expression in Human Gingival Fibroblasts.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 1;12(8):1727. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081727. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200192 Free PMC article.
-
On the osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells by a fabricated porous nano-hydroxyapatite substrate loaded with sodium fluoride.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Oct 14;24(1):1218. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04987-z. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39402484 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Whitford G.M. The metabolism and toxicity of fluoride. Monogr. Oral Sci. 1996;16:1–153. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

