Inflammation as A Precursor of Atherothrombosis, Diabetes and Early Vascular Aging
- PMID: 35055149
- PMCID: PMC8778078
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23020963
Inflammation as A Precursor of Atherothrombosis, Diabetes and Early Vascular Aging
Abstract
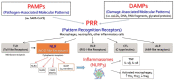
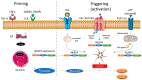
Vascular disease was for a long time considered a disease of the old age, but it is becoming increasingly clear that a cumulus of factors can cause early vascular aging (EVA). Inflammation plays a key role in vascular stiffening and also in other pathologies that induce vascular damage. There is a known and confirmed connection between inflammation and atherosclerosis. However, it has taken a long time to prove the beneficial effects of anti-inflammatory drugs on cardiovascular events. Diabetes can be both a product of inflammation and a cofactor implicated in the progression of vascular disease. When diabetes and inflammation are accompanied by obesity, this ominous trifecta leads to an increased incidence of atherothrombotic events. Research into earlier stages of vascular disease, and documentation of vulnerability to premature vascular disease, might be the key to success in preventing clinical events. Modulation of inflammation, combined with strict control of classical cardiovascular risk factors, seems to be the winning recipe. Identification of population subsets with a successful vascular aging (supernormal vascular aging-SUPERNOVA) pattern could also bring forth novel therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: COVID-19; NLPR3; SUPERNOVA; atherothrombosis; diabetes; inflammation; klotho; obesity; vascular senescence; visfatin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Damaskos C., Garmpis N., Kollia P., Mitsiopoulos G., Barlampa D., Drosos A., Patsouras A., Gravvanis N., Antoniou V., Litos A., et al. Assessing Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Diabetes: An Update. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2019;16:266–274. doi: 10.2174/1573403X15666191111123622. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

