Precision and Advanced Nano-Phytopharmaceuticals for Therapeutic Applications
- PMID: 35055257
- PMCID: PMC8778544
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12020238
Precision and Advanced Nano-Phytopharmaceuticals for Therapeutic Applications
Abstract
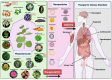
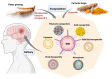
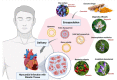
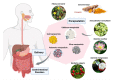
Phytopharmaceuticals have been widely used globally since ancient times and acknowledged by healthcare professionals and patients for their superior therapeutic value and fewer side-effects compared to modern medicines. However, phytopharmaceuticals need a scientific and methodical approach to deliver their components and thereby improve patient compliance and treatment adherence. Dose reduction, improved bioavailability, receptor selective binding, and targeted delivery of phytopharmaceuticals can be likely achieved by molding them into specific nano-formulations. In recent decades, nanotechnology-based phytopharmaceuticals have emerged as potential therapeutic candidates for the treatment of various communicable and non-communicable diseases. Nanotechnology combined with phytopharmaceuticals broadens the therapeutic perspective and overcomes problems associated with plant medicine. The current review highlights the therapeutic application of various nano-phytopharmaceuticals in neurological, cardiovascular, pulmonary, and gastro-intestinal disorders. We conclude that nano-phytopharmaceuticals emerge as promising therapeutics for many pathological conditions with good compliance and higher acceptance.
Keywords: herbal medications; nano-formulations; phytopharmaceuticals; precision; therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mobasser S., Firoozi A.A. Review of nanotechnology applications in science and engineering. J. Civil. Eng. Urban. 2017;64:84–93.
-
- Morelli L., Gimondi S., Sevieri M., Salvioni L., Guizzetti M., Colzani B., Palugan L., Foppoli A., Talamini L., Morosi L., et al. Monitoring the fate of orally administered PLGA nanoformulation for local delivery of therapeutic drugs. Pharmaceutics. 2019;11:658. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11120658. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

