A Predictive Model of Pandemic Disaster Fear Caused by Coronavirus (COVID-19): Implications for Decision-Makers
- PMID: 35055474
- PMCID: PMC8775677
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19020652
A Predictive Model of Pandemic Disaster Fear Caused by Coronavirus (COVID-19): Implications for Decision-Makers
Abstract
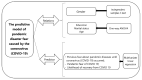
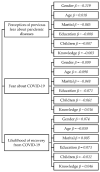
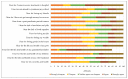
This paper presents quantitative research results regarding a predictive model of pandemic disaster fear caused by the coronavirus disease (COVİD-19). The aim of this paper was to establish the level and impact of certain demographic and socioeconomic characteristics on pandemic disaster fear caused by the coronavirus (COVID-19). The research was conducted using a questionnaire that was provided and then collected online for 1226 respondents during May 2021. A closed, five-point Likert scale was used to create the structured questionnaire. The first section of the questionnaire included research questions about the participants' socioeconomic and demographic characteristics, while the second section included issue questions about fear caused by COVID-19. The results of multivariate regression analyses showed the most important predictor for fear of COVID-19 to be gender, followed by age and education level. Furthermore, the results of t-tests showed statistically significant differences between men and women in terms of different aspects of pandemic disaster fear caused by the coronavirus disease. Our results have several significant public health implications. Women who were more educated and knowledgeable, married, and older, reported a greater fear of the outbreak at various levels. Decision-makers can use these findings to identify better strategic opportunities for pandemic disaster risk management.
Keywords: COVID-19; decision-makers; disaster; epidemic; fear; implications; pandemic; predictive model.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Wibowo Y.S., Utami R.K., Nadia Y., Nizeyumukiza E., Setiawati F.A. The fear of coronavirus disease scale: Exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis. Konselor. 2020;9:75–80. doi: 10.24036/0202092109075-0-00. - DOI
-
- Cvetković V.M. Risk Perception of Building Fires in Belgrade. Int. J. Disaster Risk Manag. 2019;1:81–91. doi: 10.18485/ijdrm.2019.1.1.5. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

