Data-Driven Construction Safety Information Sharing System Based on Linked Data, Ontologies, and Knowledge Graph Technologies
- PMID: 35055616
- PMCID: PMC8776242
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19020794
Data-Driven Construction Safety Information Sharing System Based on Linked Data, Ontologies, and Knowledge Graph Technologies
Abstract
Accident, injury, and fatality rates remain disproportionately high in the construction industry. Information from past mishaps provides an opportunity to acquire insights, gather lessons learned, and systematically improve safety outcomes. Advances in data science and industry 4.0 present new unprecedented opportunities for the industry to leverage, share, and reuse safety information more efficiently. However, potential benefits of information sharing are missed due to accident data being inconsistently formatted, non-machine-readable, and inaccessible. Hence, learning opportunities and insights cannot be captured and disseminated to proactively prevent accidents. To address these issues, a novel information sharing system is proposed utilizing linked data, ontologies, and knowledge graph technologies. An ontological approach is developed to semantically model safety information and formalize knowledge pertaining to accident cases. A multi-algorithmic approach is developed for automatically processing and converting accident case data to a resource description framework (RDF), and the SPARQL protocol is deployed to enable query functionalities. Trials and test scenarios utilizing a dataset of 200 real accident cases confirm the effectiveness and efficiency of the system in improving information access, retrieval, and reusability. The proposed development facilitates a new "open" information sharing paradigm with major implications for industry 4.0 and data-driven applications in construction safety management.
Keywords: accident prevention; construction safety; data-driven; information sharing; knowledge engineering; knowledge graph; knowledge management; linked data; ontology; semantic web.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


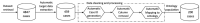

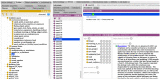






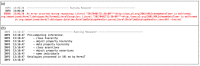
References
-
- Mckinsey Global Institute The Next Normal in Construction: How Disruption Is Reshaping the World’s Largest Ecosystem. [(accessed on 14 October 2021)]. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/operations/our-insights/the-....
-
- Pedro A., Le Q.T., Park C.S. Framework for integrating safety into construction methods education through interactive virtual reality. J. Prof. Issues Eng. Educ. Pract. 2016;142:04015011. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)EI.1943-5541.0000261. - DOI
-
- Pham H.C., Dao N.N., Cho S., Nguyen P.T., Pham-Hang A.T. Construction hazard investigation leveraging object anatomization on an augmented photoreality platform. Appl. Sci. 2019;9:4477. doi: 10.3390/app9214477. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

