Regulatory Role of Phospholipids in Hepatitis C Virus Replication and Protein Function
- PMID: 35056049
- PMCID: PMC8779051
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens11010102
Regulatory Role of Phospholipids in Hepatitis C Virus Replication and Protein Function
Abstract
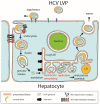
Positive-strand RNA viruses such as hepatitis C virus (HCV) hijack key factors of lipid metabolism of infected cells and extensively modify intracellular membranes to support the viral lifecycle. While lipid metabolism plays key roles in viral particle assembly and maturation, viral RNA synthesis is closely linked to the remodeling of intracellular membranes. The formation of viral replication factories requires a number of interactions between virus proteins and host factors including lipids. The structure-function relationship of those proteins is influenced by their lipid environments and lipids that selectively modulate protein function. Here, we review our current understanding on the roles of phospholipids in HCV replication and of lipid-protein interactions in the structure-function relationship of the NS5A protein. NS5A is a key factor in membrane remodeling in HCV-infected cells and is known to recruit phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase III alpha to generate phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate at the sites of replication. The dynamic interplay between lipids and viral proteins within intracellular membranes is likely key towards understanding basic mechanisms in the pathobiology of virus diseases, the mode of action of specific antiviral agents and related drug resistance mechanisms.
Keywords: NS5A; RNA virus; hepatitis C virus; interactions; membrane remodeling; phospholipid; viral replication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Romero-Brey I., Berger C., Kallis S., Kolovou A., Paul D., Lohmann V., Bartenschlager R. NS5A Domain 1 and Polyprotein Cleavage Kinetics Are Critical for Induction of Double-Membrane Vesicles Associated with Hepatitis C Virus Replication. mBio. 2015;6:e00759. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00759-15. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

