Immune Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Vaccination in Dialysis Patients and Kidney Transplant Recipients
- PMID: 35056453
- PMCID: PMC8779774
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms10010004
Immune Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Vaccination in Dialysis Patients and Kidney Transplant Recipients
Abstract
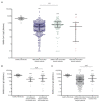
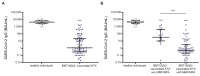
Dialysis patients and kidney transplant (KTX) recipients suffer from an impaired immune system and show a decreased response to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus type 2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccination. We performed a retrospective analysis of 1505 serological SARS-CoV-2 measurements obtained from 887 dialysis patients and 86 KTX recipients. The results were separated by patient subgroups (dialysis/KTX) as well as SARS-CoV-2 status. The latter criterion included SARS-CoV-2-naïve patients with or without COVID-19 vaccination and convalescent patients receiving a booster shot. Serologies of 27 vaccinated healthy individuals served as the reference group. Vaccine-induced cellular immune response was quantified by an interferon-γ release assay in 32 KTX recipients. We determined seroconversion rates of 92.6%, 93.4%, and 71.4% in dialysis patients vaccinated with either BNT162b2, mRNA-1273, or AZD1222, respectively. Vaccination-induced anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody titers were lower in dialysis patients compared to healthy individuals, and vaccination with mRNA-1273 induced higher titers than BNT162b2. The initial seroconversion rate was 39.5% in KTX recipients vaccinated with BNT162b2. A linear regression model identified medication with mycophenolate-mofetil/mycophenolic acid as an independent risk factor for missing seroconversion. Within a cohort of 32 KTX recipients, cellular and humoral immune reactivity to SARS-CoV-2 was detectable in three patients only. Conclusively, vaccine-induced seroconversion rates were similar in dialysis patients compared to healthy individuals but were strongly impaired in KTX recipients. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG titers elicited by double active immunization were significantly lower in both cohorts compared to healthy individuals, and immune responses to vaccination vanished quickly.
Keywords: COVID-19; antibodies; immunosuppression; kidney disease; protection; titer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
-
- Espi M., Charmetant X., Barba T., Koppe L., Pelletier C., Kalbacher E., Chalencon E., Mathias V., Ovize A., Cart-Tanneur E., et al. The ROMANOV study found impaired humoral and cellular immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine in virus-unexposed patients receiving maintenance hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 2021;100:928–936. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2021.07.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jung C., Flaatten H., Fjølner J., Bruno R.R., Wernly B., Artigas A., Bollen Pinto B., Schefold J.C., Wolff G., Kelm M., et al. The impact of frailty on survival in elderly intensive care patients with COVID-19: The COVIP study. Crit. Care. 2021;25:149. doi: 10.1186/s13054-021-03551-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

