Enzyme Activity of Natural Products on Cytochrome P450
- PMID: 35056827
- PMCID: PMC8779343
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27020515
Enzyme Activity of Natural Products on Cytochrome P450
Abstract
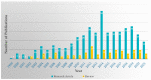
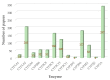
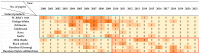
Drug-metabolizing enzymes, particularly the cytochrome P450 (CYP450) monooxygenases, play a pivotal role in pharmacokinetics. CYP450 enzymes can be affected by various xenobiotic substrates, which will eventually be responsible for most metabolism-based herb-herb or herb-drug interactions, usually involving competition with another drug for the same enzyme binding site. Compounds from herbal or natural products are involved in many scenarios in the context of such interactions. These interactions are decisive both in drug discovery regarding the synergistic effects, and drug application regarding unwanted side effects. Herein, this review was conducted as a comprehensive compilation of the effects of herbal ingredients on CYP450 enzymes. Nearly 500 publications reporting botanicals' effects on CYP450s were collected and analyzed. The countries focusing on this topic were summarized, the identified herbal ingredients affecting enzyme activity of CYP450s, as well as methods identifying the inhibitory/inducing effects were reviewed. Inhibitory effects of botanicals on CYP450 enzymes may contribute to synergistic effects, such as herbal formulae/prescriptions, or lead to therapeutic failure, or even increase concentrations of conventional medicines causing serious adverse events. Conducting this review may help in metabolism-based drug combination discovery, and in the evaluation of the safety profile of natural products used therapeutically.
Keywords: combinatorial synergism; cytochrome P450; herbal ingredient; herb–drug interaction; herb–herb interaction; natural product.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Ji S., He D.D., Su Z.Y., Du Y., Wang Y.J., Gao S.K., Guo M.Z., Tang D.Q. P450 enzymes-based metabolic interactions between monarch drugs and the other constituent herbs: A strategy to explore compatibility mechanism of Sangju-Yin. Phytomedicine. 2019;58:152866. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.152866. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ma W.J., Wang W., Huang X.H., Yao G.Z., Jia Q., Shen J.Y., Ouyang H.Z., Chang Y.X., He J. HPLC-MS/MS analysis of Aconiti Lateralis Radix praeparata and its combination with Red Ginseng effect on rat CYP450 activities using the cocktail approach. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2020;2020:8603934. doi: 10.1155/2020/8603934. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

