Vibrational Dynamics in crystalline 4-(dimethylamino) benzaldehyde: Inelastic Neutron Scattering and Periodic DFT Study
- PMID: 35057193
- PMCID: PMC8780805
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15020475
Vibrational Dynamics in crystalline 4-(dimethylamino) benzaldehyde: Inelastic Neutron Scattering and Periodic DFT Study
Abstract
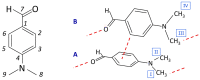
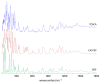
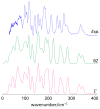
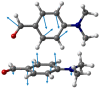
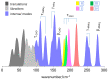
The structure and dynamics of crystalline 4-(dimethylamino) benzaldehyde, 4DMAB, are assessed through INS spectroscopy combined with periodic DFT calculations. The excellent agreement between experimental and calculated spectra is the basis for a reliable assignment of INS bands. The external phonon modes of crystalline 4DMAB are quite well described by the simulated spectrum, as well as the modes involving low-frequency molecular vibrations. Crystal field splitting is predicted and observed for the modes assigned to the dimethylamino group. Concerning the torsional motion of methyl groups, four individual bands are identified and assigned to specific methyl groups in the asymmetric unit. The torsional frequencies of the four methyl groups in the asymmetric unit fall in a region of ca. 190 ± 20 cm-1, close to the range of values observed for methyl groups bonding to unsaturated carbon atoms. The hybridization state of the X atom in X-CH3 seems to play a key role in determining the methyl torsional frequency.
Keywords: density functional theory; inelastic neutron scattering; methyl torsion; molecular crystal; vibrational assignment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Araujo C.F., Nolasco M.M., Ribeiro-Claro P.J.A., Rudić S., Silvestre A.J.D., Vaz P.D., Sousa A.F. Inside PEF: Chain conformation and dynamics in crystalline and amorphous domains. Macromolecules. 2018;51:3515–3526. doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.8b00192. - DOI
-
- Parker S.F., Butler I.R. Synthesis, computational studies, inelastic neutron scattering, infrared and raman spectroscopy of ruthenocene. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2019;2019:1142–1146. doi: 10.1002/ejic.201800914. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

