3-D printed microfluidics for rapid prototyping and testing of electrochemical, aptamer-based sensor devices under flow conditions
- PMID: 35057946
- PMCID: PMC8931854
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2021.339377
3-D printed microfluidics for rapid prototyping and testing of electrochemical, aptamer-based sensor devices under flow conditions
Abstract
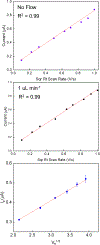
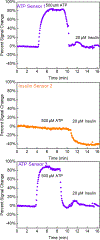
We demonstrate the ability to rapidly prototype and fabricate an epoxy-embedded electrode platform and microfluidic device suitable for using electrochemical biosensors under flow conditions. We utilize three-dimensional (3-D) printing to rapidly prototype molds to fabricate epoxy-embedded electrodes in addition to molds for rapid prototyping of PDMS microfluidic components. We characterize the bare gold epoxy-embedded electrodes using ferricyanide as a redox indicator and then characterize the performance of an adenosine triphosphate (ATP) specific electrochemical, aptamer-based (E-AB) sensor. We then incorporate the ATP specific E-AB sensors into the microfluidic device to study and take advantage of the dynamic response this class of sensor offers. We were able to flow varying concentrations of target analyte and monitor the dynamic response of the sensors to the changing concentration. This work demonstrates the ability to rapidly prototype E-AB sensors under flow conditions using 3-D printing which can lead to rapid and affordable point-of-care or fieldable applications where dynamic measurements of concentration, specificity and sensitivity and multiplex detection are necessary.
Keywords: 3-D printed microfluidic prototypes; Aptamer-based sensors; Dynamic concentration measurement; Electrochemical; Epoxyembedded electrodes.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
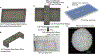
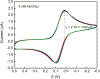
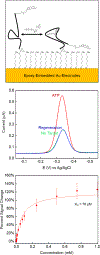
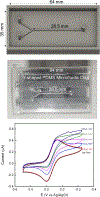
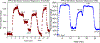
References
-
- Shaver A; Curtis SD; Arroyo-Currás N. Alkanethiol Monolayer End Groups Affect the Long-Term Operational Stability and Signaling of Electrochemical, Aptamer-Based Sensors in Biological Fluids. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12 (9), 11214–11223. - PubMed
-
- Arroyo-Currás N; Dauphin-Ducharme P; Ortega G; Ploense KL; Kippin TE; Plaxco KW Subsecond-Resolved Molecular Measurements in the Living Body Using Chronoamperometrically Interrogated Aptamer-Based Sensors. ACS Sensors. 2018, 3 (2), 360–366. - PubMed
-
- Kim K; Lee S; Ryu S; Han D. Efficient Isolation and Elution of Cellular Proteins Using Aptamer-Mediated Protein Precipitation Assay. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2014, 448 (1), 114–119. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

