Prospective Phase II Trial of Prognostication by 68Ga-NOTA-AE105 uPAR PET in Patients with Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: Implications for uPAR-Targeted Therapy
- PMID: 35058319
- PMCID: PMC9454472
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.121.263177
Prospective Phase II Trial of Prognostication by 68Ga-NOTA-AE105 uPAR PET in Patients with Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: Implications for uPAR-Targeted Therapy
Abstract
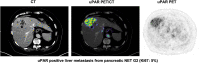
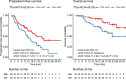
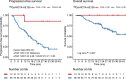
The clinical course for patients with neuroendocrine neoplasms (NENs) ranges from indolent to highly aggressive. Noninvasive tools to improve prognostication and guide decisions on treatment are warranted. Expression of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) is present in many cancer types and associated with a poor outcome. Therefore, using an in-house-developed uPAR PET tracer [68Ga]Ga-NOTA-Asp-Cha-Phe-D-Ser-D-Arg-Tyr-Leu-Trp-Ser-OH (68Ga-NOTA-AE105), we aimed to assess uPAR expression in NENs. We hypothesized that uPAR expression was detectable in a significant proportion of patients and associated with a poorer outcome. In addition, as uPAR-targeted radionuclide therapy has previously proven effective in preclinical models, the study would also indicate the potential for uPAR-targeted radionuclide therapy in NEN patients. Methods: In a prospective clinical phase II trial, we included 116 patients with NENs of all grades, of whom 96 subsequently had uPAR PET/CT performed with evaluable lesions. PET/CT was performed 20 min after injection of approximately 200 MBq of 68Ga-NOTA-AE105. uPAR target-to-liver ratio was used to define lesions as uPAR-positive when lesion SUVmax-to-liver SUVmean ratio was at least 2. Patients were followed for at least 1 y to assess progression-free and overall survival. Results: Most patients had small intestinal NENs (n = 61) and metastatic disease (n = 86). uPAR-positive lesions were seen in 68% (n = 65) of all patients and in 75% (n = 18) of patients with high-grade (grade 3) NENs. During follow-up (median, 28 mo), 59 patients (62%) experienced progressive disease and 28 patients (30%) died. High uPAR expression, defined as a uPAR target-to-liver ratio above median, had a hazard ratio of 1.87 (95% CI, 1.11-3.17) and 2.64 (95% CI, 1.19-5.88) for progression-free and overall survival, respectively (P < 0.05 for both). Conclusion: When 68Ga-NOTA-AE105 PET was used to image uPAR in patients with NENs, uPAR-positive lesions were seen in most patients, notably in patients with both low-grade and high-grade NENs. Furthermore, uPAR expression was associated with a worse prognosis. We suggest that uPAR PET is relevant for risk stratification and that uPAR may be a promising target for therapy in patients with NENs.
Keywords: PET; molecular imaging; neuroendocrine neoplasms; prognosis; urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR).
© 2022 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prospective phase II trial of [68Ga]Ga-NOTA-AE105 uPAR-PET/MRI in patients with primary gliomas: Prognostic value and Implications for uPAR-targeted Radionuclide Therapy.EJNMMI Res. 2024 Oct 29;14(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s13550-024-01164-9. EJNMMI Res. 2024. PMID: 39472354 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Value of Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Receptor PET/CT in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas and Comparison with 18F-FDG PET/CT: A Single-Center Prospective Study.J Nucl Med. 2022 Aug;63(8):1169-1176. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.121.262866. Epub 2021 Dec 2. J Nucl Med. 2022. PMID: 34857658 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Receptor as a Potential PET Biomarker in Glioblastoma.J Nucl Med. 2016 Feb;57(2):272-8. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.115.161703. Epub 2015 Oct 1. J Nucl Med. 2016. PMID: 26429955
-
Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Receptor-PET with 68Ga-NOTA-AE105: First Clinical Experience with a Novel PET Ligand.PET Clin. 2017 Jul;12(3):311-319. doi: 10.1016/j.cpet.2017.02.003. Epub 2017 Apr 8. PET Clin. 2017. PMID: 28576169 Review.
-
177Lu-Labeled DOTA-conjugated AE105 peptide (Asp-Cha-Phe-(d)Ser-(d)Arg-Tyr-Leu-Trp-Ser-CONH2).2012 Sep 13 [updated 2012 Nov 8]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2012 Sep 13 [updated 2012 Nov 8]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 23166959 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic Value of Preoperative uPAR-PET/CT in Regional Lymph Node Staging of Oral and Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Prospective Phase II Trial.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Oct 25;13(21):3303. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13213303. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37958201 Free PMC article.
-
Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Receptor (uPAR) Expression and [64Cu]Cu-DOTA-AE105 uPAR-PET/CT in Patient-Derived Xenograft Models of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Mol Imaging Biol. 2023 Dec;25(6):1034-1044. doi: 10.1007/s11307-023-01858-x. Epub 2023 Sep 25. Mol Imaging Biol. 2023. PMID: 37749438 Free PMC article.
-
Radiopharmaceuticals and their applications in medicine.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Jan 3;10(1):1. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-02041-6. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 39747850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Receptor (uPAR) Cooperates with Mutated KRAS in Regulating Cellular Plasticity and Gemcitabine Response in Pancreatic Adenocarcinomas.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Mar 3;15(5):1587. doi: 10.3390/cancers15051587. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36900379 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective phase II trial of [68Ga]Ga-NOTA-AE105 uPAR-PET/MRI in patients with primary gliomas: Prognostic value and Implications for uPAR-targeted Radionuclide Therapy.EJNMMI Res. 2024 Oct 29;14(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s13550-024-01164-9. EJNMMI Res. 2024. PMID: 39472354 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Klimstra DS, Kloppel G, La Rosa S, Rindi G. Digestive System Tumours. 5th ed. International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2019:16–19.
-
- Ahn SB, Mohamedali A, Pascovici D, et al. . Proteomics reveals cell-surface urokinase plasminogen activator receptor expression impacts most hallmarks of cancer. Proteomics. 2019;19:e1900026. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
