Structural Rigidification of N-Aryl-pyrroles into Indoles Active against Intracellular and Drug-Resistant Mycobacteria
- PMID: 35059125
- PMCID: PMC8762742
- DOI: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.1c00431
Structural Rigidification of N-Aryl-pyrroles into Indoles Active against Intracellular and Drug-Resistant Mycobacteria
Abstract
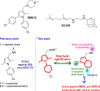
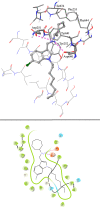
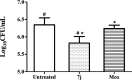
A series of indolyl-3-methyleneamines incorporating lipophilic side chains were designed through a structural rigidification approach and synthesized for investigation as new chemical entities against Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb). The screening led to the identification of a 6-chloroindole analogue 7j bearing an N-octyl chain and a cycloheptyl moiety, which displayed potent in vitro activity against laboratory and clinical Mtb strains, including a pre-extensively drug-resistant (pre-XDR) isolate. 7j also demonstrated a marked ability to restrict the intracellular growth of Mtb in murine macrophages. Further assays geared toward mechanism of action elucidation have thus far ruled out the involvement of various known promiscuous targets, thereby suggesting that the new indole 7j may inhibit Mtb via a unique mechanism.
© 2021 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . Global Tuberculosis Report; WHO, 2020. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240013131.
-
- Chakaya J.; Khan M.; Ntoumi F.; Aklillu E.; Fatima R.; Mwaba P.; Kapata N.; Mfinanga S.; Hasnain S. E.; Katoto P. D. M. C.; Bulabula A. N. H.; Sam-Agudu N. A.; Nachega J. B.; Tiberi S.; McHugh T. D.; Abubakar I.; Zumla A. Global Tuberculosis Report 2020 – Reflections on the Global TB Burden, Treatment and Prevention Efforts. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 4–9. 10.1016/j.ijid.2021.02.107. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

