Discovery of Spiro-azaindoline Inhibitors of Hematopoietic Progenitor Kinase 1 (HPK1)
- PMID: 35059127
- PMCID: PMC8762754
- DOI: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.1c00473
Discovery of Spiro-azaindoline Inhibitors of Hematopoietic Progenitor Kinase 1 (HPK1)
Abstract
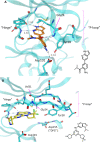
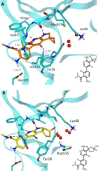
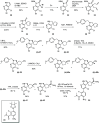
Hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 (HPK1) is implicated as a negative regulator of T-cell receptor-induced T-cell activation. Studies using HPK1 kinase-dead knock-in animals have demonstrated the loss of HPK1 kinase activity resulted in an increase in T-cell function and tumor growth inhibition in glioma models. Herein, we describe the discovery of a series of small molecule inhibitors of HPK1. Using a structure-based drug design approach, the kinase selectivity of the molecules was significantly improved by inducing and stabilizing an unusual P-loop folded binding mode. The metabolic liabilities of the initial 7-azaindole high-throughput screening hit were mitigated by addressing a key metabolic soft spot along with physicochemical property-based optimization. The resulting spiro-azaindoline HPK1 inhibitors demonstrated improved in vitro ADME properties and the ability to induce cytokine production in primary human T-cells.
© 2021 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chen D. S.; Mellman I. Oncology meets immunology: the cancer-immunity cycle. Immunity 2013, 39, 1–10. 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.07.012. - DOI - PubMed
- Barbee M. S.; Ogunniyi A.; Horvat T. Z.; Dang T.-O. Current status and future directions of the immune checkpoint inhibitors ipilimumab, pembrolizumab, and nivolumab in oncology. Ann. Pharmacother. 2015, 49, 907–937. 10.1177/1060028015586218. - DOI - PubMed
- Sharma P.; Allison J. P. Immune checkpoint targeting in cancer therapy: toward combination strategies with curative potential. Cell 2015, 161, 205–214. 10.1016/j.cell.2015.03.030. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mahoney K. M.; Rennert P. D.; Freeman G. J. Combination cancer immunotherapy and new immunomodulatory targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2015, 14, 561–584. 10.1038/nrd4591. - DOI - PubMed
- Heffron T. P.; Chan B. K. Small molecules for cancer immunotherapy. Med. Chem. Rev. 2017, 52, 219–241. 10.29200/acsmedchemrev-v52.ch12. - DOI
-
- Hernandez S.; Qing J.; Thibodeau R. H.; Du X.; Park S.; Lee H.-M.; Xu M.; Oh S.; Navarro A.; Roose-Girma M.; Newman R. J.; Warming S.; Nannini M.; Sampath D.; Kim J. M.; Grogan J. L.; Mellman I. The kinase activity of Hematopoietic Progenitor Kinase 1 is essential for the regulation of T cell function. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 80–94. 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.09.012. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sawasdikosol S.; Burakoff S. A perspective on HPK1 as a novel immuno-oncology drug target. eLife 2020, 9, e5512210.7554/eLife.55122. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Degnan A. P.; Kumi G. K.; Allard C. W.; Araujo E. V.; Johnson W. L.; Zimmermann K.; Pearce B. C.; Sheriff S.; Futran A.; Li X.; Locke G. A.; You D.; Morrison J.; Parrish K. E.; Stromko C.; Murtaza A.; Liu J.; Johnson B. M.; Vite G. D.; Wittman M. D. Discovery of Orally Active Isofuranones as Potent, Selective Inhibitors of Hematopoetic Progenitor Kinase 1. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 443–450. 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.0c00660. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Yu E. C.; Methot J. L.; Fradera X.; Lesburg C. A.; Lacey B. M.; Siliphaivanh P.; Liu P.; Smith D. M.; Xu Z.; Piesvaux J. A.; Kawamura S.; Xu H.; Miller J. R.; Bittinger M.; Pasternak A. Identification of Potent Reverse Indazole Inhibitors for HPK1. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 459–466. 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.0c00672. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Vara B. A.; Levi S. M.; Achab A.; Candito D. A.; Fradera X.; Lesburg C. A.; Kawamura S.; Lacey B. M.; Lim J.; Methot J. L.; Xu Z.; Xu H.; Smith D. M.; Piesvaux J. A.; Miller J. R.; Bittinger M.; Ranganath S. H.; Bennett D. J.; DiMauro E. F.; Pasternak A. Discovery of Diaminopyrimidine Carboxamide HPK1 inhibitors as Preclinical Immunotherapy Tool Compounds. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 653–661. 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.1c00096. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- You D.; Hillerman S.; Locke G.; Chaudhry C.; Stromko C.; Murtaza A.; Fan Y.; Koenitzer J.; Chen Y.; Briceno S.; Bhadra R.; Duperret E.; Gullo-Brown J.; Gao C.; Zhao D.; Feder J.; Curtin J.; Degnan A. P.; Kumi G.; Wittman M.; Johnson B. M.; Parrish K. E.; Gokulrangan G.; Morrison J.; Quigley M.; Hunt J. T.; Salter-Cid L.; Lees E.; Sanjuan M. A.; Liu J. Enhanced antitumor immunity by a novel small molecule HPK1 inhibitor. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e00140210.1136/jitc-2020-001402. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Linney I. D.; Kaila N. Inhibitors of immuno-oncology target HPK1 – a patent review (2016–2020). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2021, 31, 893–910. 10.1080/13543776.2021.1924671. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

