Transforming growth factor β latency: A mechanism of cytokine storage and signalling regulation in liver homeostasis and disease
- PMID: 35059619
- PMCID: PMC8760520
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2021.100397
Transforming growth factor β latency: A mechanism of cytokine storage and signalling regulation in liver homeostasis and disease
Abstract
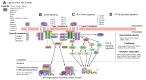
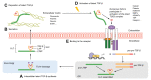
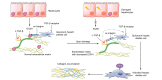
Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) is a potent effector in the liver, which is involved in a plethora of processes initiated upon liver injury. TGF-β affects parenchymal, non-parenchymal, and inflammatory cells in a highly context-dependent manner. Its bioavailability is critical for a fast response to various insults. In the liver - and probably in other organs - this is made possible by the deposition of a large portion of TGF-β in the extracellular matrix as an inactivated precursor form termed latent TGF-β (L-TGF-β). Several matrisomal proteins participate in matrix deposition, latent complex stabilisation, and activation of L-TGF-β. Extracellular matrix protein 1 (ECM1) was recently identified as a critical factor in maintaining the latency of deposited L-TGF-β in the healthy liver. Indeed, its depletion causes spontaneous TGF-β signalling activation with deleterious effects on liver architecture and function. This review article presents the current knowledge on intracellular L-TGF-β complex formation, secretion, matrix deposition, and activation and describes the proteins and processes involved. Further, we emphasise the therapeutic potential of toning down L-TGF-β activation in liver fibrosis and liver cancer.
Keywords: BMDCs, bone marrow-derived dendritic cells; BMPs, bone morphogenetic proteins; Co-Smad, co-mediator Smad; ECM, extracellular matrix; ECM1; ECM1, extracellular matrix protein 1; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; HSCs, hepatic stellate cells; I-Smad, inhibitory Smad; L-TGF-β, latent transforming growth factor β; LAP, latency-associated peptide; LLC, large latent complex; LTBP, latent TGF-β binding protein; Latent TGF-β; Liver disease; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; PAI-1, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; R-Smad, receptor-regulated Smad; RGD, arginine-glycine-aspartic acid; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SLC, small latent complex; TGF-β activation; TGF-β signalling; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β; TIMP-1, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1; TSP, thrombospondin; cFn, cellular fibronectin; cRGD, cyclic arginine-glycine-aspartic acid peptide; pFn, plasma fibronectin; rECM1, recombinant ECM1 protein; α-SMA, alpha-smooth muscle actin.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. Please refer to the accompanying ICMJE disclosure forms for further details.
Figures
References
-
- Taipale J., Saharinen J., Keski-Oja J. Extracellular matrix-associated transforming growth factor-beta: role in cancer cell growth and invasion. Adv Cancer Res. 1998;75:87–134. - PubMed
-
- Laiho M., Keski-Oja J. Transforming growth factors-beta as regulators of cellular growth and phenotype. Crit Rev Oncog. 1992;3:1–26. - PubMed
-
- Shi Y., Massague J. Mechanisms of TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell. 2003;113:685–700. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

