Comparative differential cytotoxicity of clinically used SERMs in human cancer lines of different origin and its predictive molecular docking studies of key target genes involved in cancer progression and treatment responses
- PMID: 35059624
- PMCID: PMC8760488
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crphar.2021.100080
Comparative differential cytotoxicity of clinically used SERMs in human cancer lines of different origin and its predictive molecular docking studies of key target genes involved in cancer progression and treatment responses
Abstract
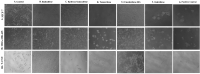
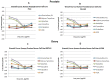
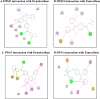
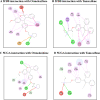
SERMS like Tamoxifene, 5-hydroxy tamoxifene, raloxifene and endoxifene has been used for the treatment of hormonal imbalances and dependent cancers owing to their action via Estrogen receptors as in the treatment of estrogen sensitive breast cancers. Due to the adverse side effects, modifications and development of the existing or newer SERMS has always been of immense interest. Ormeloxifene, a SERM molecule manufactured by HLL Lifecare Ltd, India as birth control under the trade names Saheli, Novex, and Novex-DS which is also investigated against mastalgia, fibro-adenoma and abnormal uterine bleeding. Anti-cancer effects have been reported in estrogen dependent and independent cancers which shows its wide scope to be implemented in cancer therapy. Current investigation is a comprehensive effort to find the cytotoxic potential of Ormeloxifene in comparison with clinically used four SERMS in twenty six cancer cell lines of different origin using Adriamycin as positive control. Also the computational studies pertaining to selected target/ligand with respect to tumor progression, development, treatment responses and apoptosis. The studies proved effective cytotoxicity of Ormeloxifene on cancer cell lines with lower TGI, GI50 and LC50 values which are significantly comparable. Also the in silico studies proved that the docking score of the compound suggests the interaction of the compound which could tightly regulate key target genes controlling cancer like ER, EGFR kinase, EGFR-cSRC, HDAC-2, PARP-1 and BRAF. This study brings out the superior efficacy of Ormeloxifene compared to other SERMS with proven safety profile to be repositioned as an anti-cancer drug to treat diverse cancer types.
Keywords: 5-Hydroxy tamoxifene; Cytotoxicity; Endoxifene; Ormeloxifene; Raloxifene; SERM (Selective estrogen receptor modulator); Tamoxifene.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures













Similar articles
-
Selective estrogen receptor modulators: an update on recent clinical findings.Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2008 Mar;63(3):163-81. doi: 10.1097/OGX.0b013e31816400d7. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2008. PMID: 18279543 Review.
-
Nonhormonal selective estrogen receptor modulator 1-(2-[4-{(3R,4S)-7-Methoxy-2, 2-dimethyl-3-phenyl-chroman-4yl}phenoxy]ethyl)pyrrolidine hydrochloride (ormeloxifene hydrochloride) for the treatment of breast cancer.Drug Dev Res. 2018 Sep;79(6):275-286. doi: 10.1002/ddr.21440. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Drug Dev Res. 2018. PMID: 30284735
-
Effect of ormeloxifene on ovariectomy-induced bone resorption, osteoclast differentiation and apoptosis and TGF beta-3 expression.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2006 Aug;100(4-5):117-28. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2006.03.009. Epub 2006 Jun 21. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16797179
-
SERMs and SERMs with estrogen for postmenopausal osteoporosis.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2010 Dec;11(4):253-9. doi: 10.1007/s11154-010-9137-1. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2010. PMID: 20446043 Review.
-
The cardiovascular effects of selective estrogen receptor modulators.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006 Dec;1092:374-84. doi: 10.1196/annals.1365.034. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006. PMID: 17308162 Review.
Cited by
-
Oxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidines as Anticancer Agents: A Comprehensive Review of the Literature Focusing on SAR Analysis.Molecules. 2025 Feb 3;30(3):666. doi: 10.3390/molecules30030666. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 39942770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design, synthesis and evaluation of the anti-breast cancer activity of 1,3-oxazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine and 1,3-oxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine derivatives.RSC Med Chem. 2023 Feb 16;14(4):692-699. doi: 10.1039/d2md00377e. eCollection 2023 Apr 26. RSC Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37122542 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbasi-Radmoghaddam Z., Riahi S., Gharaghani S., Mohammadi-Khanaposhtanai M. Design of potential anti-tumor PARP-1 inhibitors by QSAR and molecular modeling studies. Mol. Divers. 2021;25(1):263–277. - PubMed
-
- Adomaityte J., Farooq M., Qayyum R. Database DARE: Quality-Assessed Reviews. Centre for Reviews and Dissemination; UK): 2008. Effect of raloxifene therapy on venous thromboembolism in postmenopausal women: a meta-analysis. - PubMed
-
- Agrawal S., Ahmad H., Dwivedi M., Shukla M., Arya A., Sharma K., Lal J., Dwivedi A.K. PEGylated chitosan nanoparticles potentiate repurposing of ormeloxifene in breast cancer therapy. Nanomedicine. 2016;11(16):2147–2169. - PubMed
-
- Amé J.C., Spenlehauer C., de Murcia G. The PARP superfamily. Bioessays. 2004;26(8):882–893. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

