Defining the volume of rabies immunoglobulins/ rabies monoclonal antibodies requirement for wound infiltration of category III animal exposures - an exploratory study
- PMID: 35061550
- PMCID: PMC8903922
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2021.2013079
Defining the volume of rabies immunoglobulins/ rabies monoclonal antibodies requirement for wound infiltration of category III animal exposures - an exploratory study
Abstract
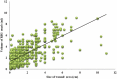
WHO recommends infiltration of rabies immunoglobulins/rabies monoclonal antibodies as anatomically possible, into or close to all category III animal bite wound(s)/exposures for post exposure prophylaxis. The volume required for wound infiltration depending upon the site/size/severity of wound is yet to be defined for guiding the treating physicians. This study aimed to determine the volume of rabies immunoglobulin/rabies monoclonal antibody required for wound infiltration depending upon the site, size, and severity. A prospective cohort study was conducted including category III animal exposures at the anti-rabies clinic, KIMS hospital and Research Center, Bangalore, India. The volume of rabies immunoglobulins/rabies monoclonal antibodies required for wound infiltration, depending on site, severity, and size was determined. All the subjects were followed for 6 months to demonstrate the safety and clinical efficacy of post exposure prophylaxis. The present study included 717 subjects having 1428 bite wounds. There was a significant difference in the median volume required for wound infiltration based on site, size, and severity of bite wounds. However, on pairwise comparison; the median volume among all the pairs for only wound size was found to be statistically significant. Supportively, a strong positive correlation was seen with the size of wound and volume infiltrated. The volume of rabies immunoglobulin/rabies monoclonal antibodies required for wound infiltration shall be determined according to size of wounds, i.e. 1 ml for <1 cm wound, 3 ml for 1-5 cm wound, and 5 ml for >5 cm wound.
Keywords: post exposure prophylaxis; rabies immunoglobulins; rabies monoclonal antibodies; volume; wound infiltration.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Weekly Epidemiological Record . Rabies Vaccines: WHO Position Paper No 16. World Health Organization; 2018. Vol. 93, p. 201–20.
-
- World Health Organization . WHO South East Asia region strategic framework for elimination of human rabies transmitted by dogs in the South-East Asia region. Geneva (Switzerland): World Health Organization, Regional office for South East Asia; 2012.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical