Sustained low disease activity measured by ASDAS slow radiographic spinal progression in axial spondyloarthritis patients treated with TNF-inhibitors: data from REGISPONSERBIO
- PMID: 35063018
- PMCID: PMC8780330
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-021-02695-5
Sustained low disease activity measured by ASDAS slow radiographic spinal progression in axial spondyloarthritis patients treated with TNF-inhibitors: data from REGISPONSERBIO
Abstract
Background: To evaluate the influence of the disease activity on radiographic progression in axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) patients treated with TNF inhibitors (TNFi).
Methods: The study included 101 axSpA patients from the Spanish Register of Biological Therapy in Spondyloarthritides (REGISPONSERBIO), which had clinical data and radiographic assessment available. Patients were classified into 2 groups based on the duration of TNFi treatment at baseline: (i) long-term treatment (≥4 years) and (ii) no long-term treatment (< 4 years). Radiographs were scored by two readers according to the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score (mSASSS) with known chronology. Disease activity differences between patients' groups at each time point were assessed using a linear mixed-effect model.
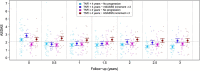
Results: Radiographic progression was defined as an increase in ≥2 mSASSS units. At inclusion, approximately half of the patients (45.5%) were receiving long-term treatment with TNFi (≥4 years). In this group of subjects, a significant difference in averaged Ankylosing Spondylitis disease Activity Score (ASDAS) across follow-up was found between progressors and non-progressors (2.33 vs 1.76, p=0.027, respectively). In patients not under long-term TNFi treatment (54.5%) though, no significant ASDAS differences were observed between progressors and non-progressors until the third year of follow-up. Furthermore, no significant differences were found in progression status, when disease activity was measured by Bath Ankylosing spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) and C reactive protein (CRP).
Conclusions: Patients on long-term TNFi treatment with a mean sustained low disease activity measures by ASDAS presented lower radiographic progression than those with active disease.
Keywords: Biological therapies; Inflammation; Outcome measures; Radiology; Spondyloarthritis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at www.icmje.org/coi_disclosure.pdf and declare no support from any organization for the submitted work, no financial relationships with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous 3 years, and no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Ramiro S, van der Heijde D, van Tubergen A, Stolwijk C, Dougados M, van den Bosch F, et al. Higher disease activity leads to more structural damage in the spine in ankylosing spondylitis: 12-year longitudinal data from the OASIS cohort. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(8):1455–1461. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205178. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

