Cellular architecture of human brain metastases
- PMID: 35063085
- PMCID: PMC8857062
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.043
Cellular architecture of human brain metastases
Abstract
Brain metastasis (BrM) is the most common form of brain cancer, characterized by neurologic disability and an abysmal prognosis. Unfortunately, our understanding of the biology underlying human BrMs remains rudimentary. Here, we present an integrative analysis of >100,000 malignant and non-malignant cells from 15 human parenchymal BrMs, generated by single-cell transcriptomics, mass cytometry, and complemented with mouse model- and in silico approaches. We interrogated the composition of BrM niches, molecularly defined the blood-tumor interface, and revealed stromal immunosuppressive states enriched with infiltrated T cells and macrophages. Specific single-cell interrogation of metastatic tumor cells provides a framework of 8 functional cell programs that coexist or anticorrelate. Collectively, these programs delineate two functional BrM archetypes, one proliferative and the other inflammatory, that are evidently shaped through tumor-immune interactions. Our resource provides a foundation to understand the molecular basis of BrM in patients with tumor cell-intrinsic and host environmental traits.
Keywords: CyTOF; blood tumor barrier; human metastasis; metastasis-associated macrophages; metastasis-infiltrated T cells; metastatic niche; metastatic program; metastatic tumor cells; metastatic tumors; single cell.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



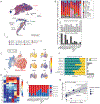

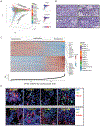

Comment in
-
Brain metastases: Not all tumors are created equal.Neuron. 2022 Apr 6;110(7):1097-1099. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.03.027. Neuron. 2022. PMID: 35390289
References
-
- Achrol AS, Rennert RC, Anders C, Soffietti R, Ahluwalia MS, Nayak L, Peters S, Arvold ND, Harsh GR, Steeg PS, et al. (2019). Brain metastases. Nat Rev Dis Primers 5, 5. - PubMed
-
- Angerer P, Haghverdi L, Buttner M, Theis FJ, Marr C, and Buettner F (2016). destiny: diffusion maps for large-scale single-cell data in R. Bioinformatics 32, 1241–1243. - PubMed
-
- Bae S, Bessho Y, Hojo M, and Kageyama R (2000). The bHLH gene Hes6, an inhibitor of Hes1, promotes neuronal differentiation. Development 127, 2933–2943. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

