Cytokine profiles in the detection of severe lung involvement in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: The IL-8/IL-32 axis
- PMID: 35063722
- PMCID: PMC8765080
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2022.155804
Cytokine profiles in the detection of severe lung involvement in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: The IL-8/IL-32 axis
Abstract
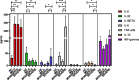
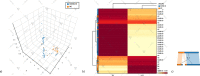
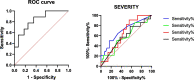
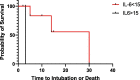
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an infectious respiratory disorder caused by a new coronavirus called SARS-CoV-2. The pathophysiology of severe COVID-19 is associated with a "cytokine storm". IL-32 is a key modulator in the pathogenesis of various clinical conditions and is mostly induced by IL-8. IL-32 modulates important inflammatory pathways (including TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1b), contributing to the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases. Il-32 was never evaluated before in COVID-19 patients stratifying as mild-moderate and severe patients. A total of 64 COVID-19 patients, 27 healthy controls were consecutively enrolled in the study. Serum concentrations of biomarkers including IL-1β, IL-10, IFN-γ, TNF-α and IL-6 were quantified by bead-based multiplex analysis and Serum concentration of IL-8 and IL-32 were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits. Interestingly, among the blood parameters, neutrophil and lymphocyte counts were significantly lower in severe COVID-19 patients than in the other, on the contrary, CRP was significantly higher in severe patients than in other groups. The cytokines that best distinguished controls from COVID-19 patients were IL-8 and IL-32, while IL-6 resulted the better variables for discriminate severe group. The best model performance for severe group was obtained by the combination of IL-32, IL-6, IFN-γ, and CRP serum concentration showing an AUC = 0.83. A cut off of 15 pg/ml of IL-6 greatly discriminate survivor from death patients. New insights related to the cytokine storm in COVID-19 patients, highlighting different severity of disease infection.
Keywords: COVID19; Cytokines; Interleukins; Profiles.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cytokine profiling in Iranian patients with COVID-19; association with clinical severity.Iran J Immunol. 2021 Mar;18(1):54-64. doi: 10.22034/iji.2021.87630.1810. Iran J Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33787514
-
Altered serum concentrations of IL-8, IL-32 and IL-10 in patients with lung impairment 6 months after COVID-19.Immunobiology. 2024 Jul;229(4):152813. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2024.152813. Epub 2024 May 24. Immunobiology. 2024. PMID: 38805808
-
High Levels of Circulating IL-8 and Soluble IL-2R Are Associated With Prolonged Illness in Patients With Severe COVID-19.Front Immunol. 2021 Jan 29;12:626235. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.626235. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33584733 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the COVID-19 cytokine storm: Systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Clin Invest. 2021 Jan;51(1):e13429. doi: 10.1111/eci.13429. Epub 2020 Nov 2. Eur J Clin Invest. 2021. PMID: 33058143 Free PMC article.
-
Critical Determinants of Cytokine Storm and Type I Interferon Response in COVID-19 Pathogenesis.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2021 May 12;34(3):e00299-20. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00299-20. Print 2021 Jun 16. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2021. PMID: 33980688 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biomarker Profiles Associated with COVID-19 Severity and Mortality.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Mar 1;45(3):1998-2012. doi: 10.3390/cimb45030128. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36975498 Free PMC article.
-
Is There a Similarity in Serum Cytokine Profile between Patients with Periodontitis or 2019-Novel Coronavirus Infection?-A Scoping Review.Biology (Basel). 2023 Apr 4;12(4):550. doi: 10.3390/biology12040550. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37106750 Free PMC article.
-
Midkine (MDK) in cancer and drug resistance: from inflammation to therapy.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jun 11;16(1):1062. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02941-1. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40500394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection of Severe Lung Infection on Chest Radiographs of COVID-19 Patients: Robustness of AI Models across Multi-Institutional Data.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Feb 5;14(3):341. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14030341. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38337857 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Interleukin-8 Dynamics Parallels Disease Course and Is Linked to Clinical Outcomes in Severe COVID-19.Viruses. 2023 Feb 16;15(2):549. doi: 10.3390/v15020549. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36851762 Free PMC article.
References
-
- d'Alessandro M., Cameli P., Refini R.M., Bergantini L., Alonzi V., Lanzarone N., Bennett D., Rana G.D., Montagnani F., Scolletta S., Franchi F., Frediani B., Valente S., Mazzei M.A., Bonella F., Bargagli E. Serum KL-6 concentrations as a novel biomarker of severe COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 2020;92(10):2216–2220. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26087. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- From the American Association of Neurological Surgeons (AANS), American Society of Neuroradiology (ASNR), Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiology Society of Europe (CIRSE), Canadian Interventional Radiology Association (CIRA), Congress of Neurological Surgeons (CNS), European Society of Minimally Invasive Neurological Therapy (ESMINT), European Society of Neuroradiology (ESNR), European Stroke Organization (ESO), Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI), Society of Interventional Radiology (SIR), Society of NeuroInterventional Surgery (SNIS), and World Stroke Organization (WSO), D. Sacks, B. Baxter, B.C.V. Campbell, J.S. Carpenter, C. Cognard, D. Dippel, M. Eesa, U. Fischer, K. Hausegger, J.A. Hirsch, M. Shazam Hussain, O. Jansen, M.V. Jayaraman, A.A. Khalessi, B.W. Kluck, S. Lavine, P.M. Meyers, S. Ramee, D.A. Rüfenacht, C.M. Schirmer, D. Vorwerk, Multisociety Consensus Quality Improvement Revised Consensus Statement for Endovascular Therapy of Acute Ischemic Stroke, Int J Stroke. 13 (2018) 612–632. 10.1177/1747493018778713. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

