What amount of structural damage defines sacroiliitis: a CT study
- PMID: 35064092
- PMCID: PMC8785200
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2021-001939
What amount of structural damage defines sacroiliitis: a CT study
Abstract
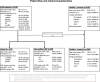
Objectives: To propose a data-driven definition for structural changes of sacroiliac (SI) joints in the context of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) imaging on a large collective of CT datasets.
Methods: 546 individuals (102 axSpA, 80 non-axSpA low back pain and 364 controls without back pain) with SI joint CTs were evaluated for erosions, sclerosis and ankylosis using a structured scoring system. Lesion frequencies and spatial distribution were compared between groups. Diagnostic performance (sensitivity (SE), specificity (SP), positive predictive values, negative predictive values and positive and negative likelihood ratios) was calculated for different combinations of imaging findings. Clinical diagnosis served as standard of reference.
Results: Ankylosis and/or erosions of the middle and dorsal joint portions yielded the best diagnostic performance with SE 67.6% and SP 96.3%. Inclusion of ventral erosions and sclerosis resulted in lower diagnostic performance with SE 71.2%/SP 92.5% and SE 70.6%/SP 90.0%, respectively.
Conclusions: Sclerosis and ventrally located erosions of SI joints have lower specificity on CT of the SI joint in the context of axSpA imaging. Ankylosis and/or erosions of the middle and dorsal joint portions show a strong diagnostic performance and are appropriate markers of a positive SI joint by CT.
Keywords: ankylosing spondylitis; ankylosis; erosion; low back pain; sclerosis.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: KGAH reports lecture fees from AbbVie, MSD and Novartis outside the submitted work. KZ reports funding (research grant) from the Assessment of Spondyloarthritis international Society (ASAS) during the conduct of this study. DP reports grants and personal fees from AbbVie, Eli Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer and personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Roche, UCB, Biocad, GlaxoSmithKline, Gilead, Janssen, Samsung Bioepis and UCB outside the submitted work. FP reports grants and personal fees from Novartis, Lilly and UCB, as well as personal fees from AbbVie, AMGEN, BMS, Hexal, MSD, Pfizer and Roche outside the submitted work. JS reports personal fees from AbbVie, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, UCB and Lilly, outside the submitted work. TD reports funding (research grant) from the ASAS and lecture fees from Canon Medical, AbbVie, MSD and Novartis pharma, outside the submitted work. For all other authors, none were reported.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
