Activation of the plant mevalonate pathway by extracellular ATP
- PMID: 35064110
- PMCID: PMC8783019
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-28150-w
Activation of the plant mevalonate pathway by extracellular ATP
Abstract
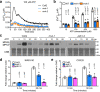
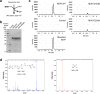
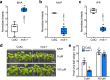
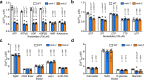
The mevalonate pathway plays a critical role in multiple cellular processes in both animals and plants. In plants, the products of this pathway impact growth and development, as well as the response to environmental stress. A forward genetic screen of Arabidopsis thaliana using Ca2+-imaging identified mevalonate kinase (MVK) as a critical component of plant purinergic signaling. MVK interacts directly with the plant extracellular ATP (eATP) receptor P2K1 and is phosphorylated by P2K1 in response to eATP. Mutation of P2K1-mediated phosphorylation sites in MVK eliminates the ATP-induced cytoplasmic calcium response, MVK enzymatic activity, and suppresses pathogen defense. The data demonstrate that the plasma membrane associated P2K1 directly impacts plant cellular metabolism by phosphorylation of MVK, a key enzyme in the mevalonate pathway. The results underline the importance of purinergic signaling in plants and the ability of eATP to influence the activity of a key metabolite pathway with global effects on plant metabolism.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
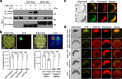
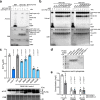
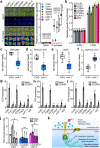
Similar articles
-
Arabidopsis Lectin Receptor Kinase P2K2 Is a Second Plant Receptor for Extracellular ATP and Contributes to Innate Immunity.Plant Physiol. 2020 Jul;183(3):1364-1375. doi: 10.1104/pp.19.01265. Epub 2020 Apr 28. Plant Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32345768 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the CNGC2-CNGC4 channel complex by P2K1-mediated phosphorylation links extracellular ATP perception to calcium signaling in plant immunity.Mol Plant. 2025 Jul 7;18(7):1130-1142. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2025.06.001. Epub 2025 Jun 4. Mol Plant. 2025. PMID: 40474480
-
CPK28 is a modulator of purinergic signaling in plant growth and defense.Plant J. 2024 May;118(4):1086-1101. doi: 10.1111/tpj.16656. Epub 2024 Feb 3. Plant J. 2024. PMID: 38308597 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanism of Plant Recognition of Extracellular ATP.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1051:233-253. doi: 10.1007/5584_2017_110. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29064066 Review.
-
Mevalonate Pathway Blockade, Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Autophagy: A Possible Link.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Jul 15;16(7):16067-84. doi: 10.3390/ijms160716067. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26184189 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identifying Receptor Kinase Substrates Using an 8000 Peptide Kinase Client Library Enriched for Conserved Phosphorylation Sites.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2025 Mar;24(3):100926. doi: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2025.100926. Epub 2025 Feb 7. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2025. PMID: 39923935 Free PMC article.
-
Salt stress releases extracellular ATP to activate purinergic signaling and inhibit plant growth.Plant Physiol. 2023 Oct 26;193(3):1753-1757. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiad429. Plant Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37506300 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular ATP: an emerging multifaceted regulator of plant fitness.Plant Biotechnol J. 2025 May;23(5):1771-1782. doi: 10.1111/pbi.70006. Epub 2025 Feb 12. Plant Biotechnol J. 2025. PMID: 39937654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ATP homeostasis and signaling in plants.Plant Commun. 2024 Apr 8;5(4):100834. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2024.100834. Epub 2024 Feb 7. Plant Commun. 2024. PMID: 38327057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Raf-like MAPKKK INTEGRIN-LINKED KINASE 5 regulates purinergic receptor-mediated innate immunity in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2023 Apr 20;35(5):1572-1592. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koad029. Plant Cell. 2023. PMID: 36762404 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Istvan ES, Deisenhofer J. Structural mechanism for statin inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase. Science. 2001;292:1160–1164. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein JL, Brown MS. Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature. 1990;343:425–430. - PubMed
-
- Buhaescu I, Izzedine H. Mevalonate pathway: a review of clinical and therapeutical implications. Clin. Biochem. 2007;40:575–584. - PubMed
-
- van der Meer JW, Simon A. The challenge of autoinflammatory syndromes: with an emphasis on hyper-IgD syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2016;55:ii23–ii29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

