Tissue-specific multi-omics analysis of atrial fibrillation
- PMID: 35064145
- PMCID: PMC8782899
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-27953-1
Tissue-specific multi-omics analysis of atrial fibrillation
Abstract
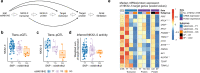
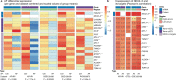
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) for atrial fibrillation (AF) have uncovered numerous disease-associated variants. Their underlying molecular mechanisms, especially consequences for mRNA and protein expression remain largely elusive. Thus, refined multi-omics approaches are needed for deciphering the underlying molecular networks. Here, we integrate genomics, transcriptomics, and proteomics of human atrial tissue in a cross-sectional study to identify widespread effects of genetic variants on both transcript (cis-eQTL) and protein (cis-pQTL) abundance. We further establish a novel targeted trans-QTL approach based on polygenic risk scores to determine candidates for AF core genes. Using this approach, we identify two trans-eQTLs and five trans-pQTLs for AF GWAS hits, and elucidate the role of the transcription factor NKX2-5 as a link between the GWAS SNP rs9481842 and AF. Altogether, we present an integrative multi-omics method to uncover trans-acting networks in small datasets and provide a rich resource of atrial tissue-specific regulatory variants for transcript and protein levels for cardiovascular disease gene prioritization.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
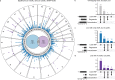
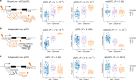
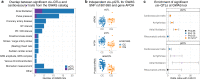
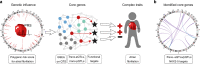
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

