Peer support for discharge from inpatient mental health care versus care as usual in England (ENRICH): a parallel, two-group, individually randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 35065722
- PMCID: PMC8776565
- DOI: 10.1016/S2215-0366(21)00398-9
Peer support for discharge from inpatient mental health care versus care as usual in England (ENRICH): a parallel, two-group, individually randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background: High numbers of patients discharged from psychiatric hospital care are readmitted within a year. Peer support for discharge has been suggested as an approach to reducing readmission post-discharge. Implementation has been called for in policy, however, evidence of effectiveness from large rigorous trials is missing. We aimed to establish whether peer support for discharge reduces readmissions in the year post-discharge.
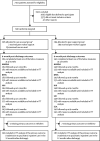
Methods: We report a parallel, two-group, individually randomised, controlled superiority trial, with trial personnel masked to allocation. Patients were adult psychiatric inpatients (age ≥18 years) with at least one previous admission in the preceding 2 years, excluding those who had a diagnosis of any organic mental disorder, or a primary diagnosis of learning disability, an eating disorder, or drug or alcohol dependency, recruited from seven state-funded mental health services in England. Patients were randomly assigned (1:1) to the intervention (peer support plus care as usual) or control (care as usual) groups by an in-house, online randomisation service, stratified by site and diagnostic group (psychotic disorders, personality disorders, and other eligible non-psychotic disorders) with randomly permuted blocks of randomly varying length to conceal the allocation sequence and achieve the allocation ratio. The peer support group received manual-based, one-to-one peer support, focused on building individual strengths and engaging with activities in the community, beginning during the index admission and continuing for 4 months after discharge, plus care as usual. Care as usual consisted of follow-up by community mental health services within 7 days of discharge. The primary outcome was psychiatric readmission 12 months after discharge (number of patients readmitted at least once), analysed on an intention-to-treat basis. All patients were included in a safety analysis, excluding those who withdrew consent for use of their data. The trial is registered with the ISRCTN registry, ISRCTN10043328. The trial was complete at the time of reporting.
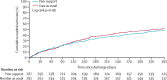
Findings: Between Dec 1, 2016, and Feb 8, 2019, 590 patients were recruited and randomly assigned, with 294 allocated to peer support (287 included in the analysis after withdrawals and loss to follow-up), and 296 to care as usual (291 in the analysis). Mean age was 39·7 years (SD 13·7; range 18-75). 306 patients were women, 267 were men, three were transgender, and two preferred not to say. 353 patients were White, 94 were Black, African, Caribbean, or Black British, 68 were Asian or Asian British, 48 were of mixed or multiple ethnic groups, and 13 were of other ethnic groups. In the peer support group, 136 (47%) of 287 patients were readmitted at least once within 12 months of discharge. 146 (50%) of 291 were readmitted in the care as usual group. The adjusted risk ratio of readmission was 0·97 (95% CI 0·82-1·14; p=0·68), and the adjusted odds ratio for readmission was 0·93 (95% CI 0·66-1·30; p=0·68). The unadjusted risk difference was 0·03 (95% CI -0·11 to 0·05; p=0·51) in favour of the peer support group. Serious adverse events were infrequent (67 events) and similar between groups (34 in the peer support group, 33 in the care as usual group). Threat to life (self-harm) was the most common serious adverse event (35 [52%] of 67 serious adverse events). 391 other adverse events were reported, with self-harm (not life threatening) the most common (189 [48%] of 391).
Interpretation: One-to-one peer support for discharge from inpatient psychiatric care, plus care as usual, was not superior to care as usual alone in the 12 months after discharge. This definitive, high-quality trial addresses uncertainty in the evidence base and suggests that peer support should not be implemented to reduce readmission post-discharge for patients at risk of readmission. Further research needs to be done to improve engagement with peer support in high-need groups, and to explore differential effects of peer support for people from different ethnic communities.
Funding: UK National Institute for Health Research.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests We declare no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Peer support for discharge from inpatient mental health care.Lancet Psychiatry. 2022 Jul;9(7):541-542. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(22)00101-8. Lancet Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35717961 No abstract available.
References
-
- Donisi V, Tedeschi F, Salazzari D, Amaddeo F. Pre- and post-discharge factors influencing early readmission to acute psychiatric wards: implications for quality-of-care indicators in psychiatry. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2016;39:53–58. - PubMed
-
- Wheeler A, Moyle S, Jansen C, Robinson E, Vanderpyl J. Five-year follow-up of an acute psychiatric admission cohort in Auckland, New Zealand. N Z Med J. 2011;124:30–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

