Parents' Maltreatment Histories, Dimensions of Emotion Regulation, and Connections to Offspring Self-Regulation: A Sex-Specific Transmission Pathway
- PMID: 35068669
- PMCID: PMC8782250
- DOI: 10.1007/s10862-021-09881-4
Parents' Maltreatment Histories, Dimensions of Emotion Regulation, and Connections to Offspring Self-Regulation: A Sex-Specific Transmission Pathway
Abstract
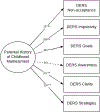
Introduction: Parents with childhood maltreatment histories are at risk for emotion regulation (ER) problems, which are associated with reduced self-regulation among their offspring. However, gaps remain in the literature regarding this indirect transmission pathway. First, ER consists of multiple dimensions and it is unclear which dimension is most affected by childhood maltreatment. Second, less is known regarding which parental ER dimension is linked to offspring self-regulation. Thus, the present study aimed to examine the direct and indirect associations between parental maltreatment histories and child self-regulatory capacity via dimensions of parental ER.
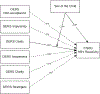
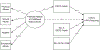
Methods: In this cross-sectional study, 101 youth (75% African American/Black; 53% female; M age = 10.28; SD = 1.19) and their primary caregivers were recruited from a low-income community in the Southeastern United States. Structural equation modeling was used to model the effect of parents' self-reported childhood maltreatment on youth physiological self-regulation (measured by heart rate variability reactivity [HRV-R]), via parents' self-reported ER.
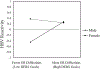
Results: Parental maltreatment history was significantly associated with five of the six components of ER. Further, the indirect effect of parents' childhood maltreatment on child HRV-R was significant when parents reported more difficulty engaging goal-directed behaviors. Moderation analyses by sex showed that daughters had greater dysregulation regardless of parental maltreatment histories, while parents' ER was found to play a more significant role in the intergenerational transmission of dysregulation to sons.
Conclusions: The current study extends the literature on self-regulation development in children of low-income, maltreatment-exposed parents. Our study may inform parent-child interventions for improving self-regulation.
Keywords: childhood maltreatment history; emotion regulation; heart rate variability; intergenerational effects of maltreatment; moderated mediation; sex differences.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Intergenerational effects of childhood maltreatment: The roles of parents' emotion regulation and mentalization.Child Abuse Negl. 2022 Jun;128:104940. doi: 10.1016/j.chiabu.2021.104940. Epub 2021 Jan 24. Child Abuse Negl. 2022. PMID: 33500161
-
The role of maternal child maltreatment history and unsupportive emotion socialization in the intergenerational transmission of emotion regulation difficulties.Child Abuse Negl. 2022 Jul;129:105661. doi: 10.1016/j.chiabu.2022.105661. Epub 2022 May 9. Child Abuse Negl. 2022. PMID: 35550482
-
Intergenerational associations between childhood maltreatment, post-traumatic stress symptoms, and chronic pain in young adult offspring and their parents.Stress Health. 2024 Oct;40(5):e3441. doi: 10.1002/smi.3441. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Stress Health. 2024. PMID: 38949630
-
The role of parental emotion reactivity and regulation in child maltreatment and maltreatment risk: A meta-analytic review.Clin Psychol Rev. 2021 Dec;90:102099. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2021.102099. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Clin Psychol Rev. 2021. PMID: 34752992 Review.
-
The transition to parenthood following a history of childhood maltreatment: a review of the literature on prospective and new parents' experiences.Eur J Psychotraumatol. 2018 Aug 2;8(Suppl 7):1492834. doi: 10.1080/20008198.2018.1492834. Eur J Psychotraumatol. 2018. PMID: 33488997 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Relationship between Paternal Alexithymia and Children's Internalizing and Externalizing Behavioral Problems during Early Childhood.Children (Basel). 2023 Sep 1;10(9):1498. doi: 10.3390/children10091498. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37761459 Free PMC article.
-
Intergenerational Effects of Childhood Maltreatment: Role of Emotion Dysregulation and Emotion Socialization.J Child Fam Stud. 2023 Jul;32(7):2187-2197. doi: 10.1007/s10826-023-02608-x. Epub 2023 Jun 8. J Child Fam Stud. 2023. PMID: 40761747 Free PMC article.
-
Emotion regulation as mediator between childhood adversity and psychopathology: A meta-analysis.Clin Psychol Rev. 2022 Apr;93:102141. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2022.102141. Epub 2022 Feb 21. Clin Psychol Rev. 2022. PMID: 35219929 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anda RF, Felitti VJ, Bremner JD, Walker JD, Whitfield C, Perry BD, Dube SR, & Giles WH (2006, Apr). The enduring effects of abuse and related adverse experiences in childhood. A convergence of evidence from neurobiology and epidemiology. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, 256(3), 174–186. 10.1007/s00406-005-0624-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Appelhans BM, & Luecken LJ (2006). Heart rate variability as an index of regulated emotional responding. Review of General Psychology, 10(3), 229–240. 10.1037/1089-2680.10.3.229 - DOI
-
- Barlow DH, Farchione TJ, Sauer-Zavala S, Murray Latin H, Ellard KK, Bullis JR, Bentley KH, Boettcher HT, & Cassiello-Robbins C (2018). Unified protocol for transdiagnostic treatment of emotional disorders (Second ed.). Oxford University Press.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
