A Current Understanding of Bile Acids in Chronic Liver Disease
- PMID: 35068796
- PMCID: PMC8766695
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jceh.2021.08.017
A Current Understanding of Bile Acids in Chronic Liver Disease
Abstract
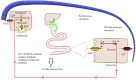
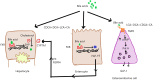
Chronic liver disease (CLD) is one of the leading causes of disability-adjusted life years in many countries. A recent understanding of nuclear bile acid receptor pathways has increased focus on the impact of crosstalk between the gut, bile acids, and liver on liver pathology. While conventionally used in cholestatic disorders and to dissolve gallstones, the discovery of bile acids' influence on the gut microbiome and human metabolism offers a unique potential for their utility in early and advanced liver diseases because of diverse etiologies. Based on these findings, preclinical studies using bile acid-based molecules have shown encouraging results at addressing liver inflammation and fibrosis. Emerging data also suggest that bile acid profiles change distinctively across various causes of liver disease. We summarize the current knowledge and evidence related to bile acids in health and disease and discuss culminated and ongoing therapeutic trials of bile acid derivatives in CLD. In the near future, further evidence in this area might help clinicians better detect and manage liver diseases.
Keywords: AD, Acute decompensation; ALP, Alkaline phosphatase; AMACR, α-methylacyl-CoA racemase (AMACR); ASBT, Apical sodium dependent bile salt transporter; BA, Bile acid; BSEP, Bile salt export pump; BSH, Bile salt hydrolase; CA, Cholic acid; CDCA, Chenodeoxycholic acid; CLD; CLD, Chronic Liver Disease; CTP, Child-Turcotte-Pugh; CYP7A1, Cholesterol 7 α hydroxylase; DCA, Deoxycholic acid; DR5, Death receptor 5; ELF, Enhanced Liver Fibrosis; FGF-19, Fibroblast growth factor-19; FGFR4, FGF receptor 4; FXR, Farnesoid X receptor; GCA, Glycocholic acid; GDCA, Glycodeoxycholic acid; GLP-1, Glucagon-like peptide1; HBV, Hepatitis B virus; HCV, Hepatitis C virus; HVPG, Hepatic Venous Pressure Gradient; LCA, Lithocholic acid; LPS, Lipopolysaccharide; MELD, Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD); MRI-PDFF, Magnetic resonance imaging derived proton density fat fraction; NAFLD; NAFLD, Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; NAS, NAFLD activity score; NASH, Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; NTCP, Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide; OCA, Obeticholic acid; OST, Organic solute transporter; PBC, Primary biliary cirrhosis; PFIC, Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis; PSC, Primary sclerosing cholangitis; PXR, Pregnane X receptor; SHP, Small heterodimer partner; TBA, Total bile acids; TGR5, Takeda G-protein coupled receptor 5; TRAIL, TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand; UDCA, Ursodeoxycholic acid; UPLC-MS, Ultra-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry; VDR, Vitamin D receptor; bile acids; cirrhosis; microbiome.
© 2021 Indian National Association for Study of the Liver. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- The Top 10 Causes of Death. Accessed May 28, 2021. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

