From Synapses to Circuits, Astrocytes Regulate Behavior
- PMID: 35069124
- PMCID: PMC8772456
- DOI: 10.3389/fncir.2021.786293
From Synapses to Circuits, Astrocytes Regulate Behavior
Abstract
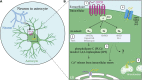
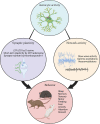
Astrocytes are non-neuronal cells that regulate synapses, neuronal circuits, and behavior. Astrocytes ensheath neuronal synapses to form the tripartite synapse where astrocytes influence synapse formation, function, and plasticity. Beyond the synapse, recent research has revealed that astrocyte influences on the nervous system extend to the modulation of neuronal circuitry and behavior. Here we review recent findings on the active role of astrocytes in behavioral modulation with a focus on in vivo studies, primarily in mice. Using tools to acutely manipulate astrocytes, such as optogenetics or chemogenetics, studies reviewed here have demonstrated a causal role for astrocytes in sleep, memory, sensorimotor behaviors, feeding, fear, anxiety, and cognitive processes like attention and behavioral flexibility. Current tools and future directions for astrocyte-specific manipulation, including methods for probing astrocyte heterogeneity, are discussed. Understanding the contribution of astrocytes to neuronal circuit activity and organismal behavior will be critical toward understanding how nervous system function gives rise to behavior.
Keywords: GPCR; astrocyte; behavior; chemogenetic; optogenetic.
Copyright © 2022 Lyon and Allen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Agarwal A., Wu P. H., Hughes E. G., Fukaya M., Tischfield M. A., Langseth A. J., et al. (2017). Transient opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore induces microdomain calcium transients in astrocyte processes. Neuron 93 587.e587–605.e587. 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.12.034 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

