Mobile Genetic Elements Drive Antimicrobial Resistance Gene Spread in Pasteurellaceae Species
- PMID: 35069478
- PMCID: PMC8777487
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.773284
Mobile Genetic Elements Drive Antimicrobial Resistance Gene Spread in Pasteurellaceae Species
Abstract
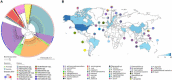
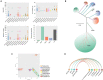
Mobile genetic elements (MGEs) and antimicrobial resistance (AMR) drive important ecological relationships in microbial communities and pathogen-host interaction. In this study, we investigated the resistome-associated mobilome in 345 publicly available Pasteurellaceae genomes, a large family of Gram-negative bacteria including major human and animal pathogens. We generated a comprehensive dataset of the mobilome integrated into genomes, including 10,820 insertion sequences, 2,939 prophages, and 43 integrative and conjugative elements. Also, we assessed plasmid sequences of Pasteurellaceae. Our findings greatly expand the diversity of MGEs for the family, including a description of novel elements. We discovered that MGEs are comparable and dispersed across species and that they also co-occur in genomes, contributing to the family's ecology via gene transfer. In addition, we investigated the impact of these elements in the dissemination and shaping of AMR genes. A total of 55 different AMR genes were mapped to 721 locations in the dataset. MGEs are linked with 77.6% of AMR genes discovered, indicating their important involvement in the acquisition and transmission of such genes. This study provides an uncharted view of the Pasteurellaceae by demonstrating the global distribution of resistance genes linked with MGEs.
Keywords: bacterial resistance; gene transfer; genome evolution; mobile DNA; one health.
Copyright © 2022 da Silva, Gonçalves, Rosa, França, Bossé, Santana, Langford and Bazzolli.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Evolution and Diversity of the Antimicrobial Resistance Associated Mobilome in Streptococcus suis: A Probable Mobile Genetic Elements Reservoir for Other Streptococci.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016 Oct 7;6:118. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00118. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27774436 Free PMC article.
-
The ESKAPE mobilome contributes to the spread of antimicrobial resistance and CRISPR-mediated conflict between mobile genetic elements.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 11;51(1):236-252. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1220. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36610752 Free PMC article.
-
In silico analyses of diversity and dissemination of antimicrobial resistance genes and mobile genetics elements, for plasmids of enteric pathogens.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jan 26;13:1095128. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1095128. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36777021 Free PMC article.
-
The Dynamics of the Antimicrobial Resistance Mobilome of Salmonella enterica and Related Enteric Bacteria.Front Microbiol. 2022 Mar 31;13:859854. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.859854. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35432284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolution of horizontal transmission in antimicrobial resistance plasmids.Microbiology (Reading). 2022 Jul;168(7). doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001214. Microbiology (Reading). 2022. PMID: 35849537 Review.
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Respiratory Bacteria from Weaned Dairy Heifers.Pathogens. 2024 Apr 3;13(4):300. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13040300. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 38668255 Free PMC article.
-
The Arms Race Between Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae and Its Genetic Environment: A Comprehensive Analysis of Its Defensome and Mobile Genetic Elements.Mol Microbiol. 2025 Jul;124(1):40-53. doi: 10.1111/mmi.15374. Epub 2025 May 3. Mol Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40317571 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic analysis reveals the role of integrative and conjugative elements in plant pathogenic bacteria.Mob DNA. 2022 Aug 12;13(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s13100-022-00275-1. Mob DNA. 2022. PMID: 35962419 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity of mobile genetic elements in carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales isolated from the intensive care units of a tertiary care hospital in Northeast India.Front Microbiol. 2025 May 22;16:1543427. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1543427. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40475381 Free PMC article.
-
Nanopore adaptive sampling effectively enriches bacterial plasmids.mSystems. 2024 Mar 19;9(3):e0094523. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00945-23. Epub 2024 Feb 20. mSystems. 2024. PMID: 38376263 Free PMC article.
References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

